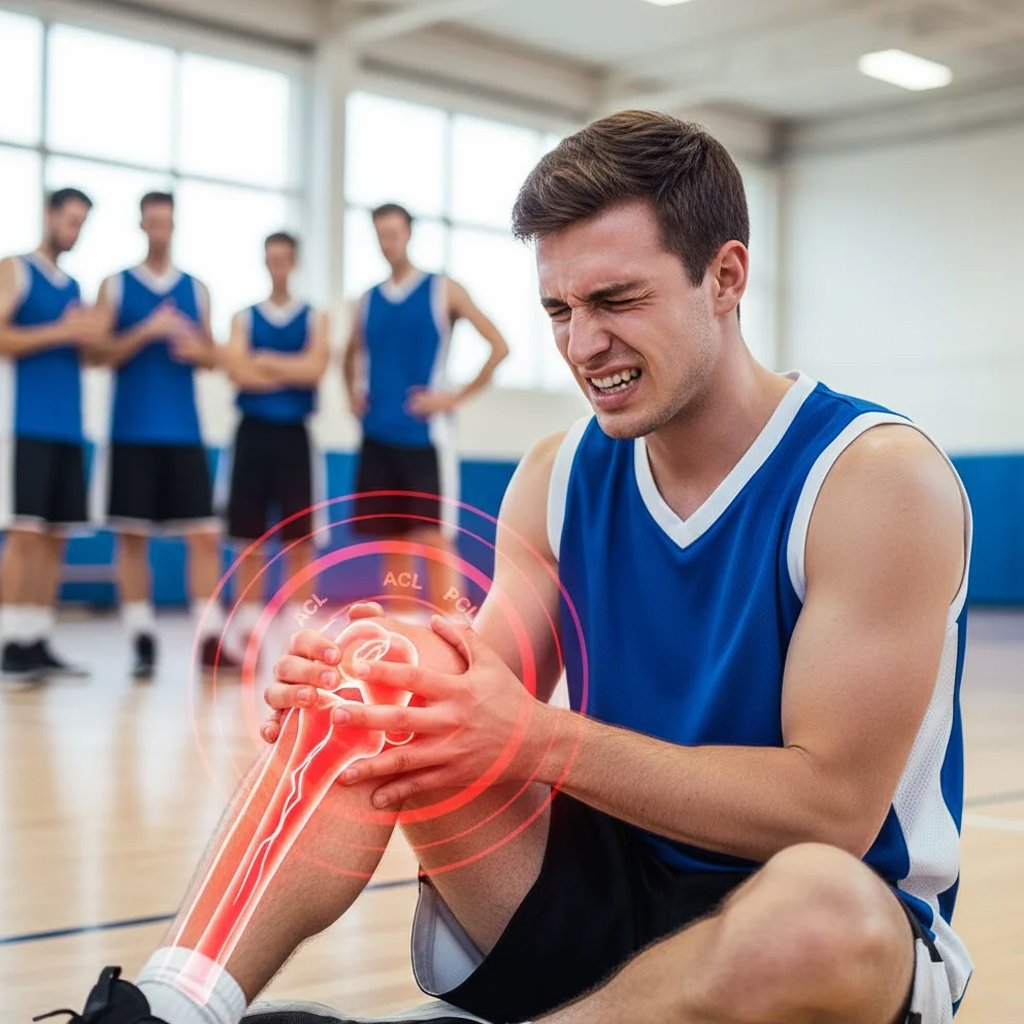
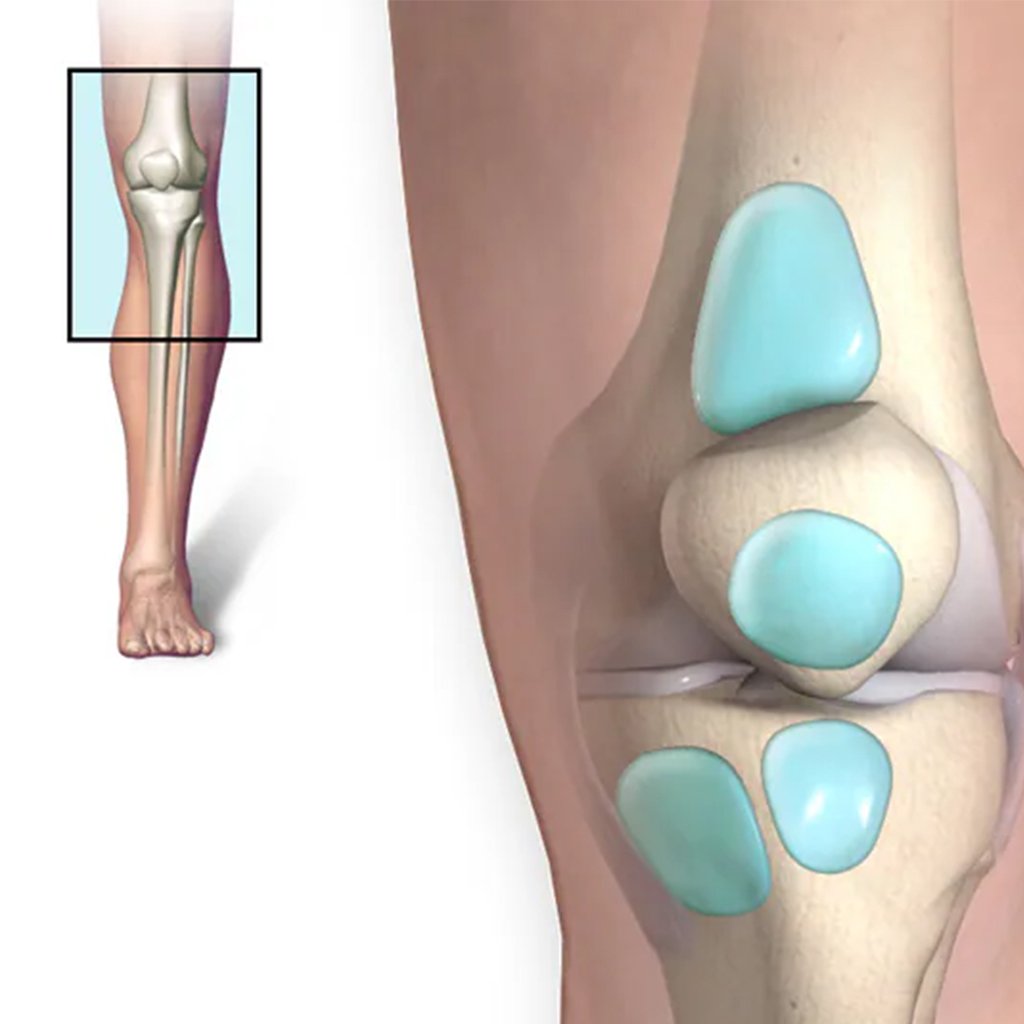
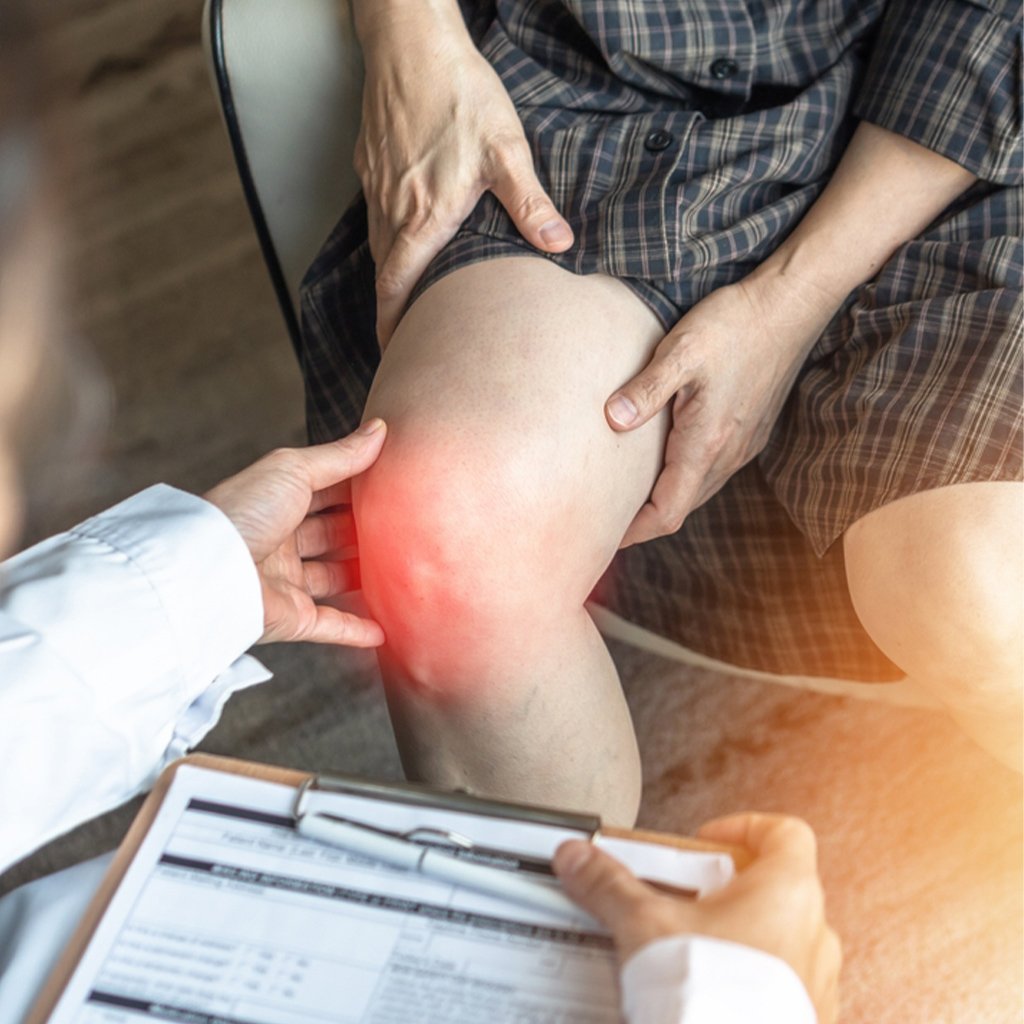
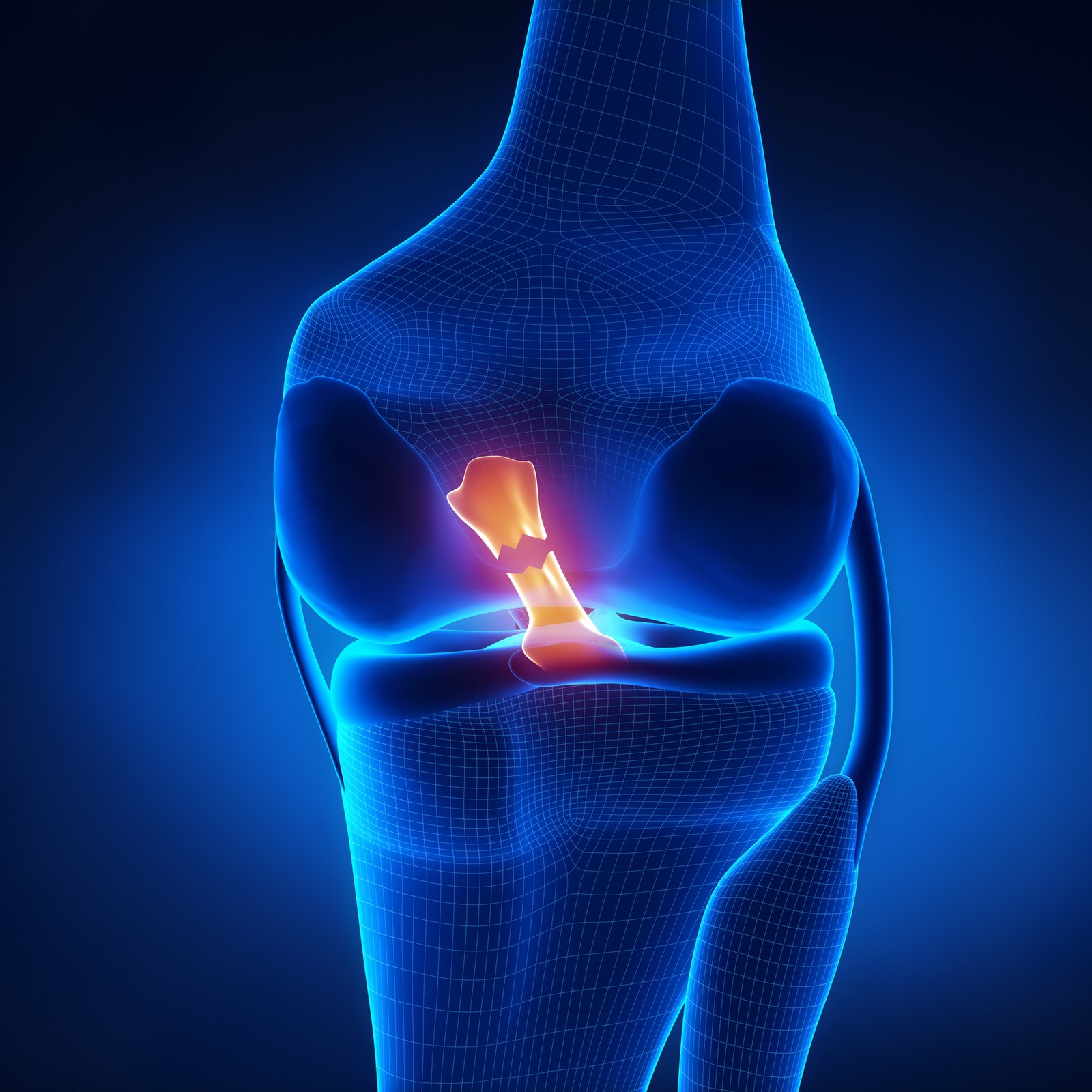
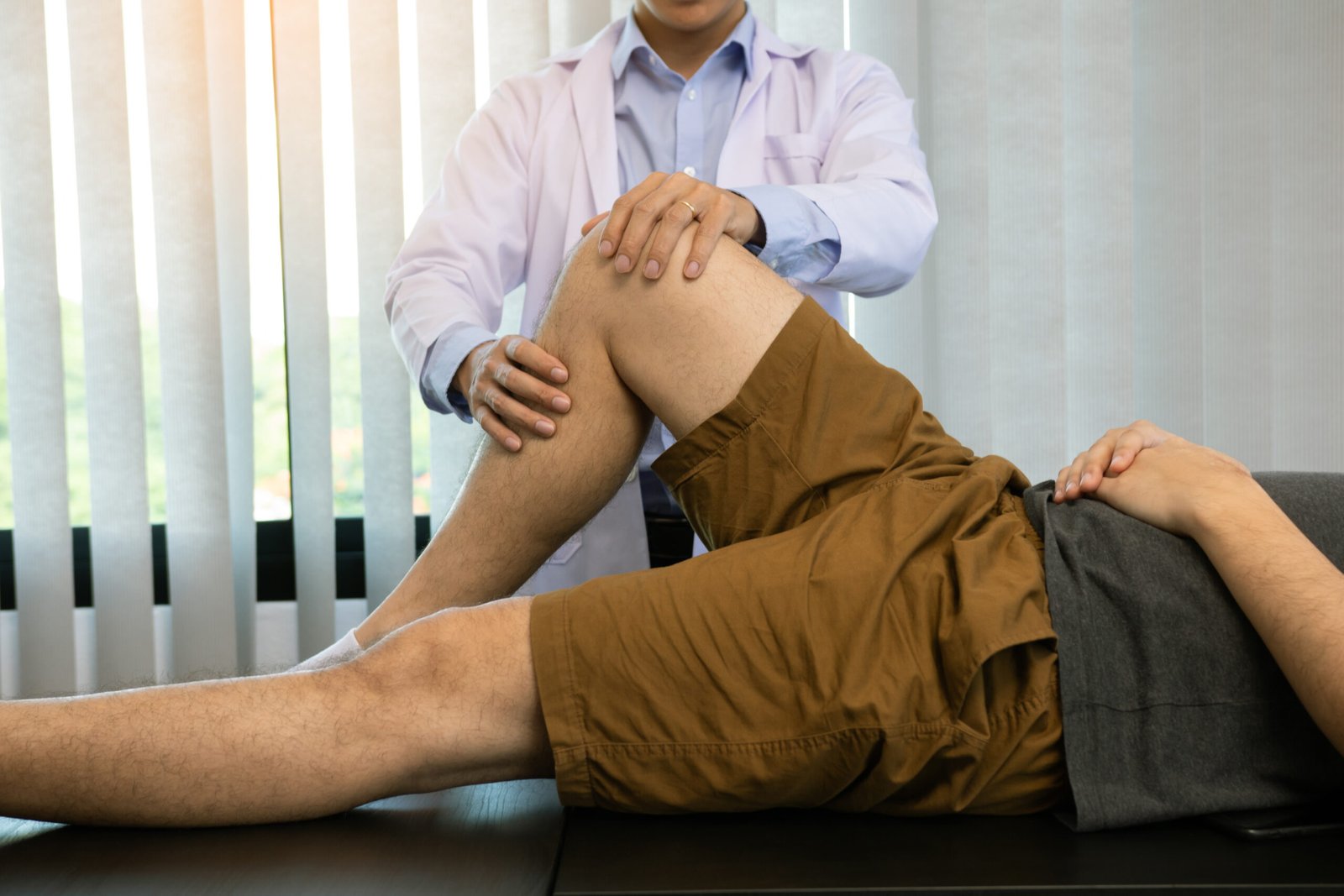
Understanding Knee Anatomy
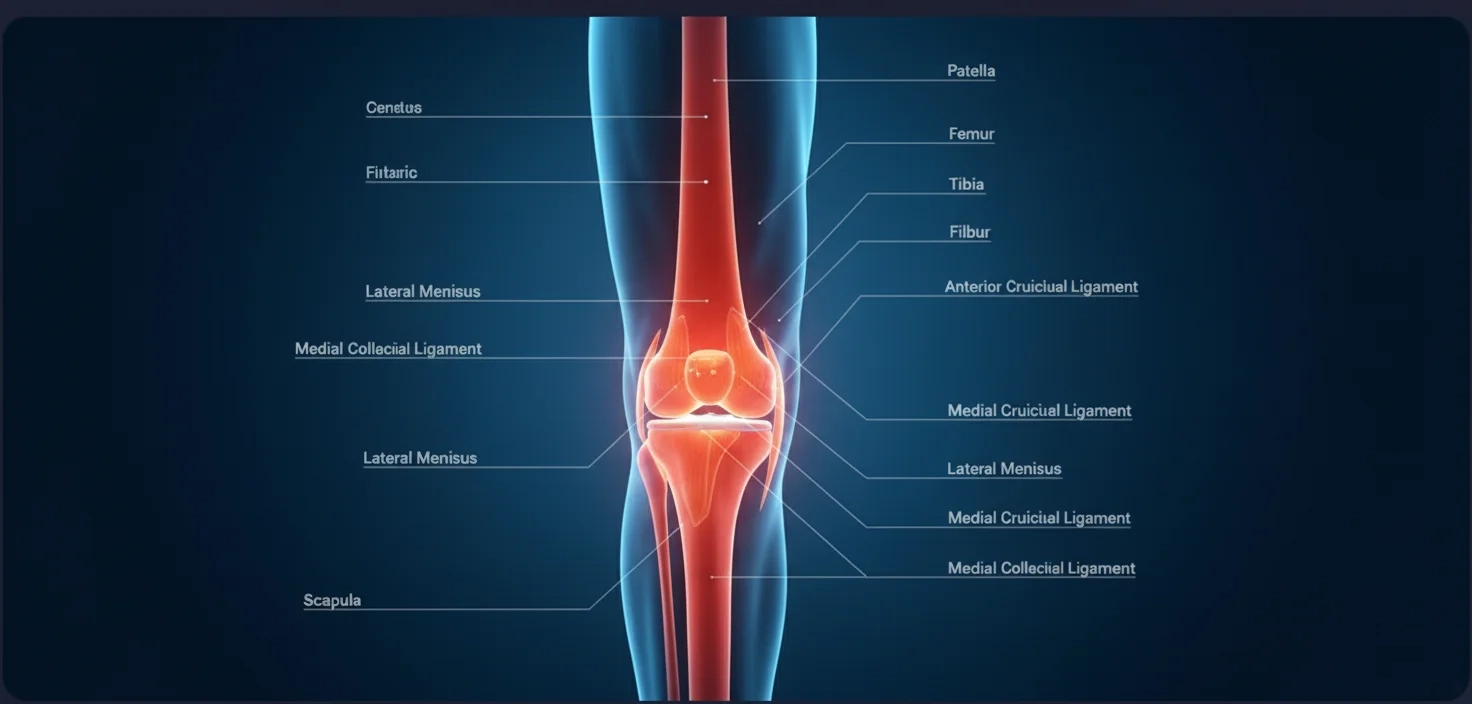
The structure and anatomy of the knee are important in guiding the causes of pain. The knee has bones (tibia, femur, patella), shock-absorbing cartilages, the menisci, ligaments (ACL, PCL, MCL, LCL), tendons, and supportive muscles. The sections are aligned with each other to facilitate steady flexion, locomotion, and standing. All the structures are susceptible to being damaged or inflamed, and this causes pain, mechanical symptoms, or instability. This is being solved through a diagnostic and curative protocol, which is offered by our team of knee pain experts. Individualised treatment of knee pain in Bangalore will be possible by providing correct anatomical knowledge.
Best Clinic in Banglore For all Knee Pain Conditions
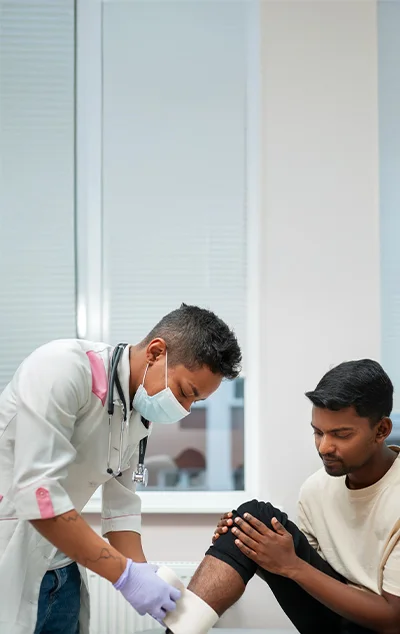
Alleviate Pain Clinic is one of the best centres that provide non-surgical treatment of knee pain in Bangalore. We have specialisation in a variety of disorders of the knees, including:
When to See a Doctor for Knee Pain
Consultation with a healthcare professional is advisable if one experiences:

Inability to bear weight or a feeling of instability.

Significant swelling or visible deformity.

Fever accompanying redness and warmth, suggesting infection.

Persistent pain is unresponsive to initial self-care measures.
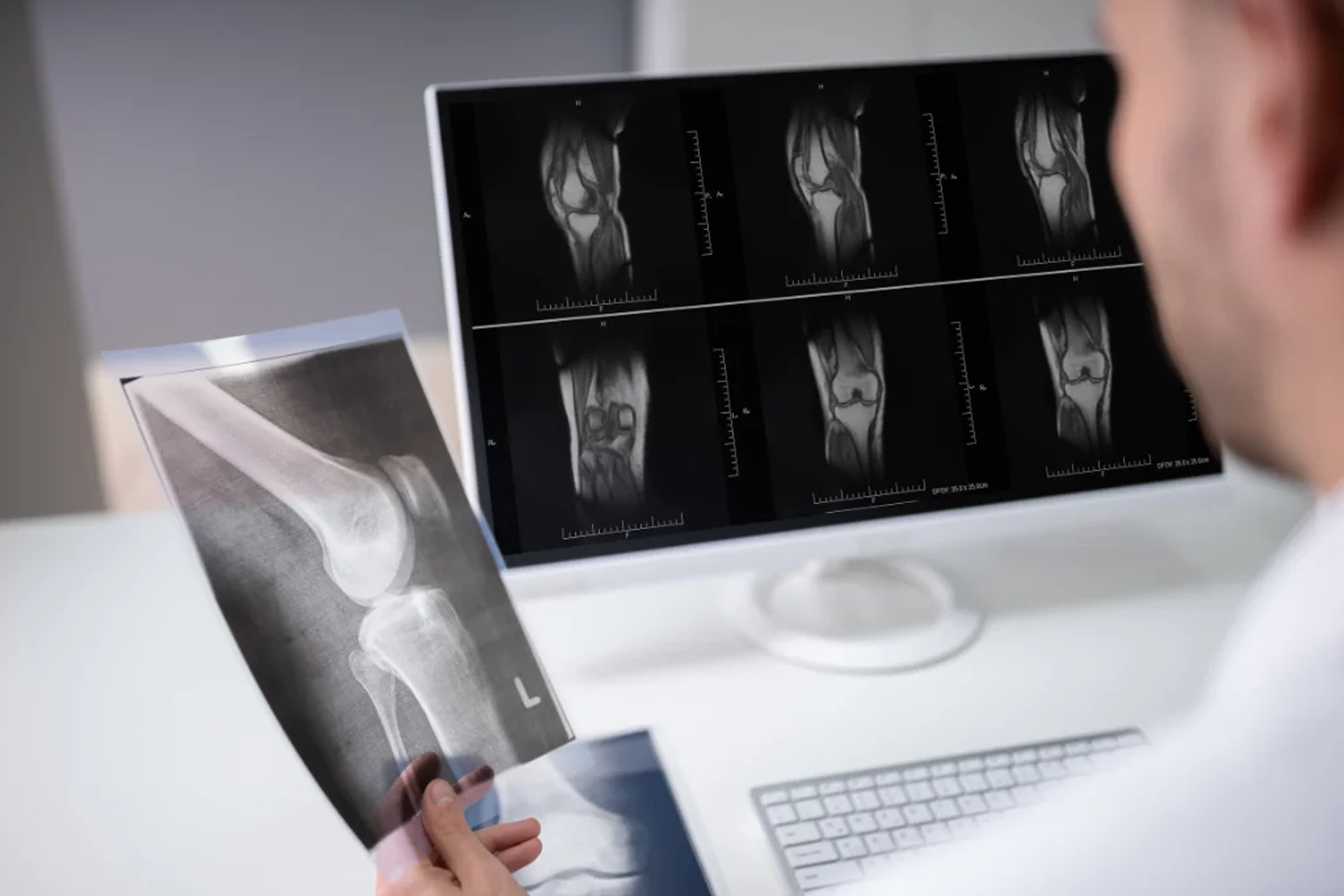
Knee Pain Diagnosis
Our Approach To Non-Surgical Knee Pain Treatment
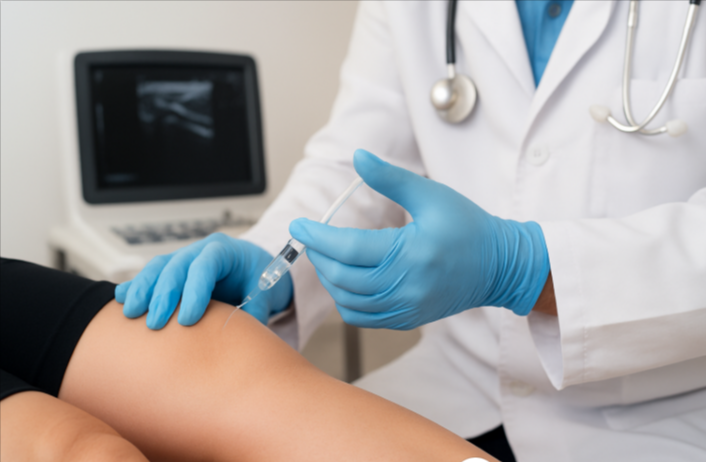
Nerve Blocks
Nerve blocks involve precisely injecting an anesthetic near specific nerves to interrupt pain signals. This procedure provides immediate relief and helps us diagnose the exact source of your discomfort.
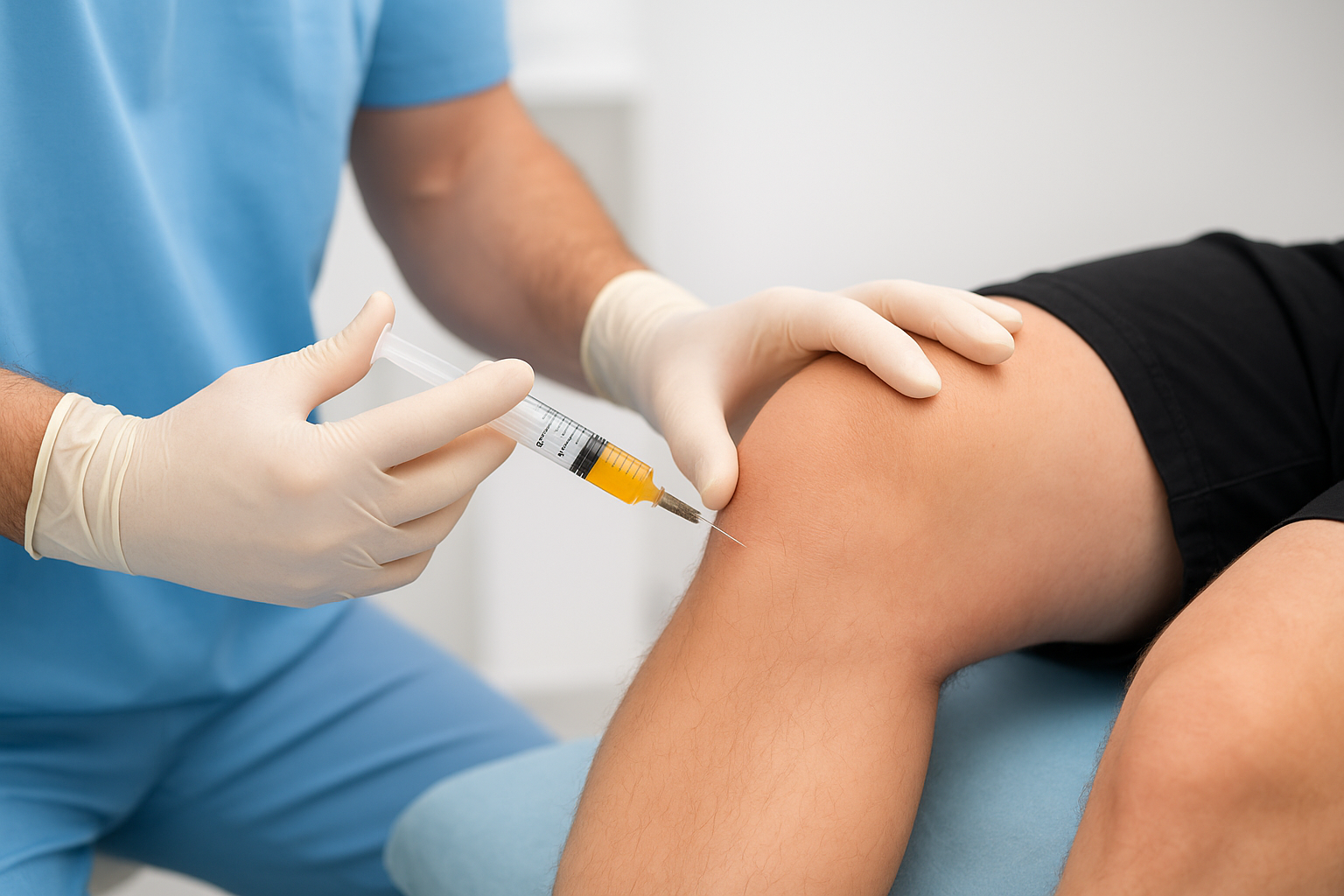
PRP (Platelet Rich Plasma Therapy)
PRP therapy uses a concentration of your own blood platelets to accelerate the healing of injured tendons, ligaments, muscles, and joints, promoting natural tissue repair and reducing inflammation.
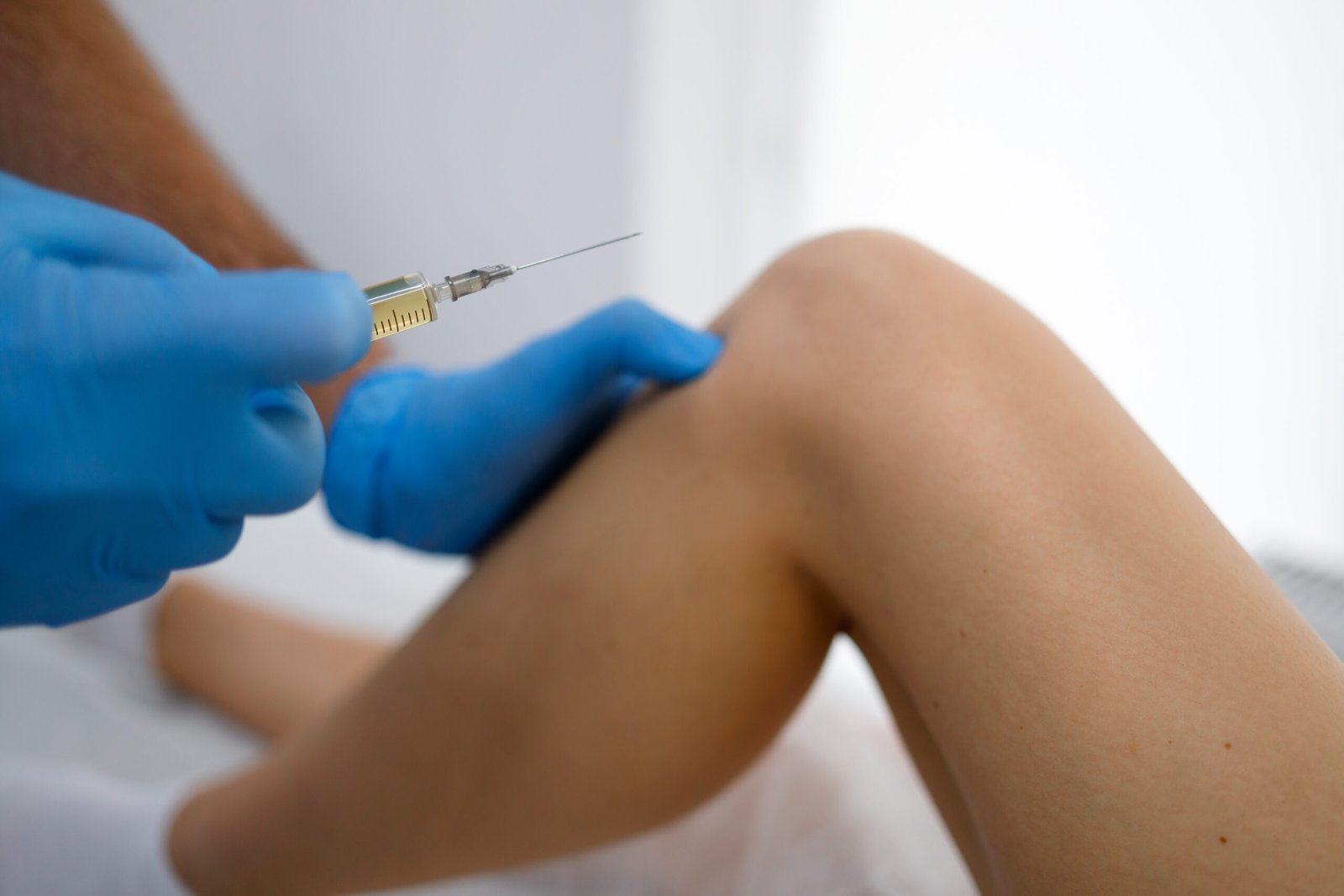
Prolotherapy
Prolotherapy is a regenerative injection therapy that stimulates the body’s natural healing process to strengthen and repair weak or injured ligaments and tendons, providing long-term pain relief.
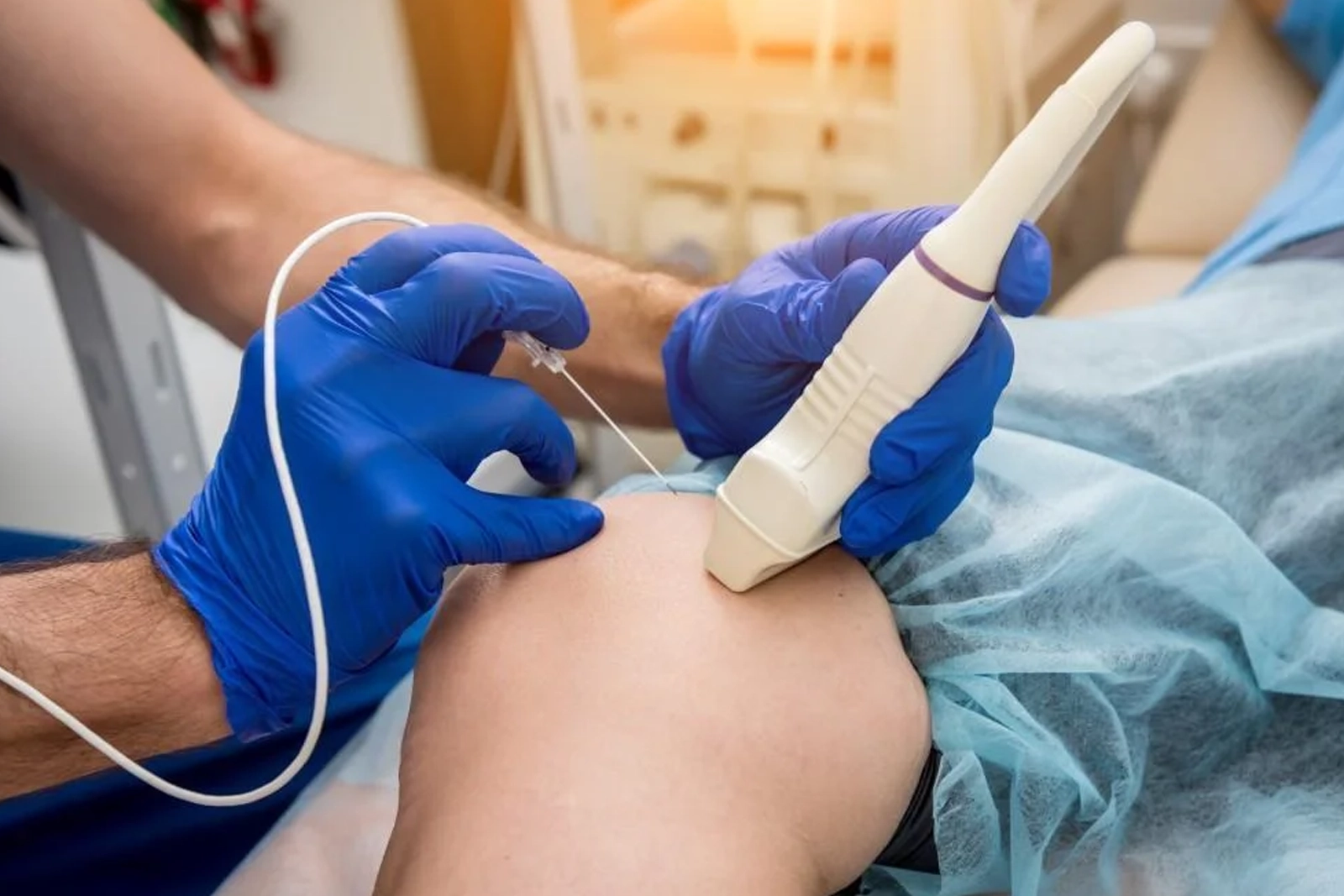
Radiofrequency
This minimally invasive procedure uses heat generated from radio waves to target specific nerves, effectively blocking pain signals from reaching the brain and offering lasting relief from chronic conditions.
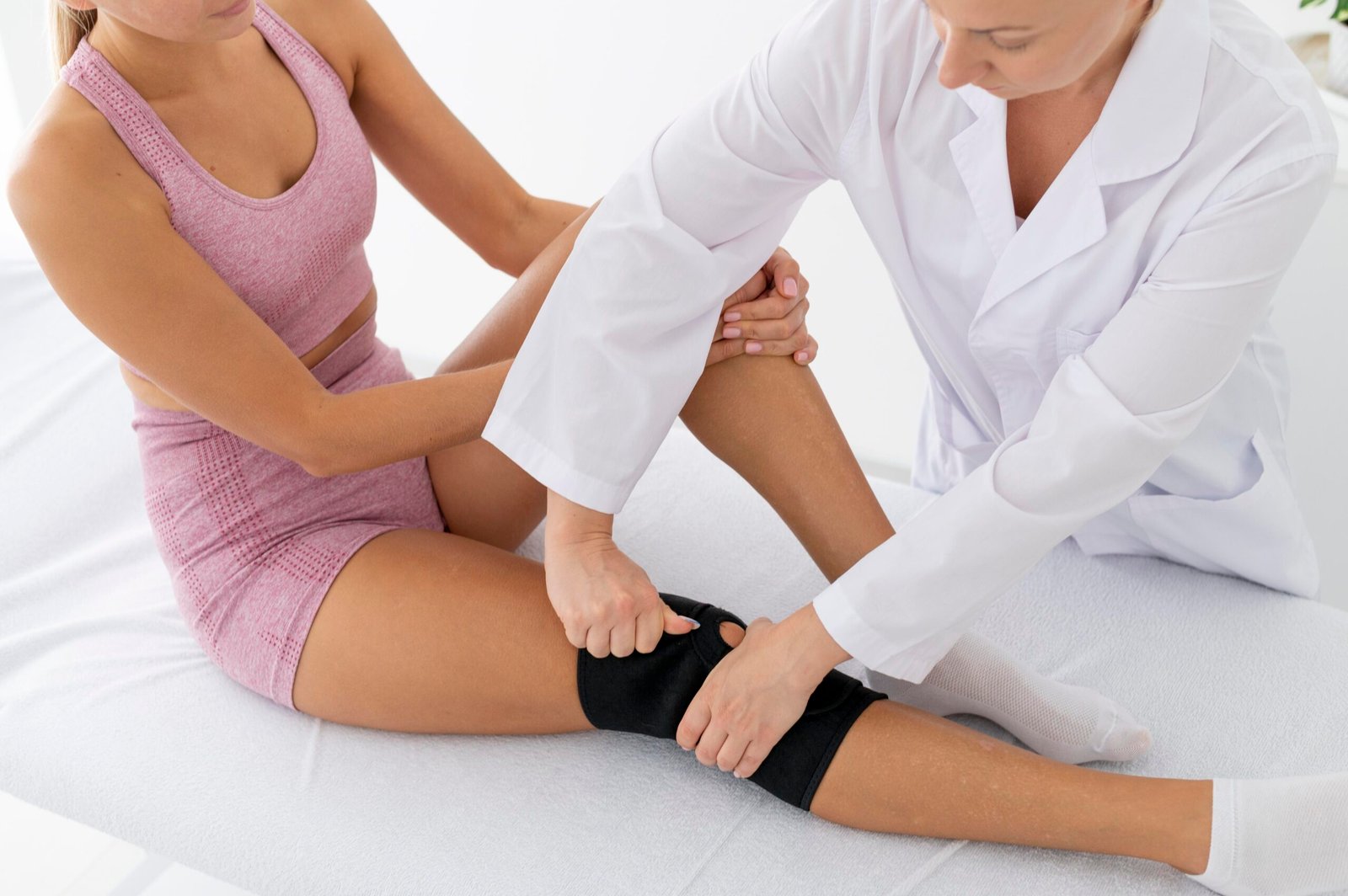
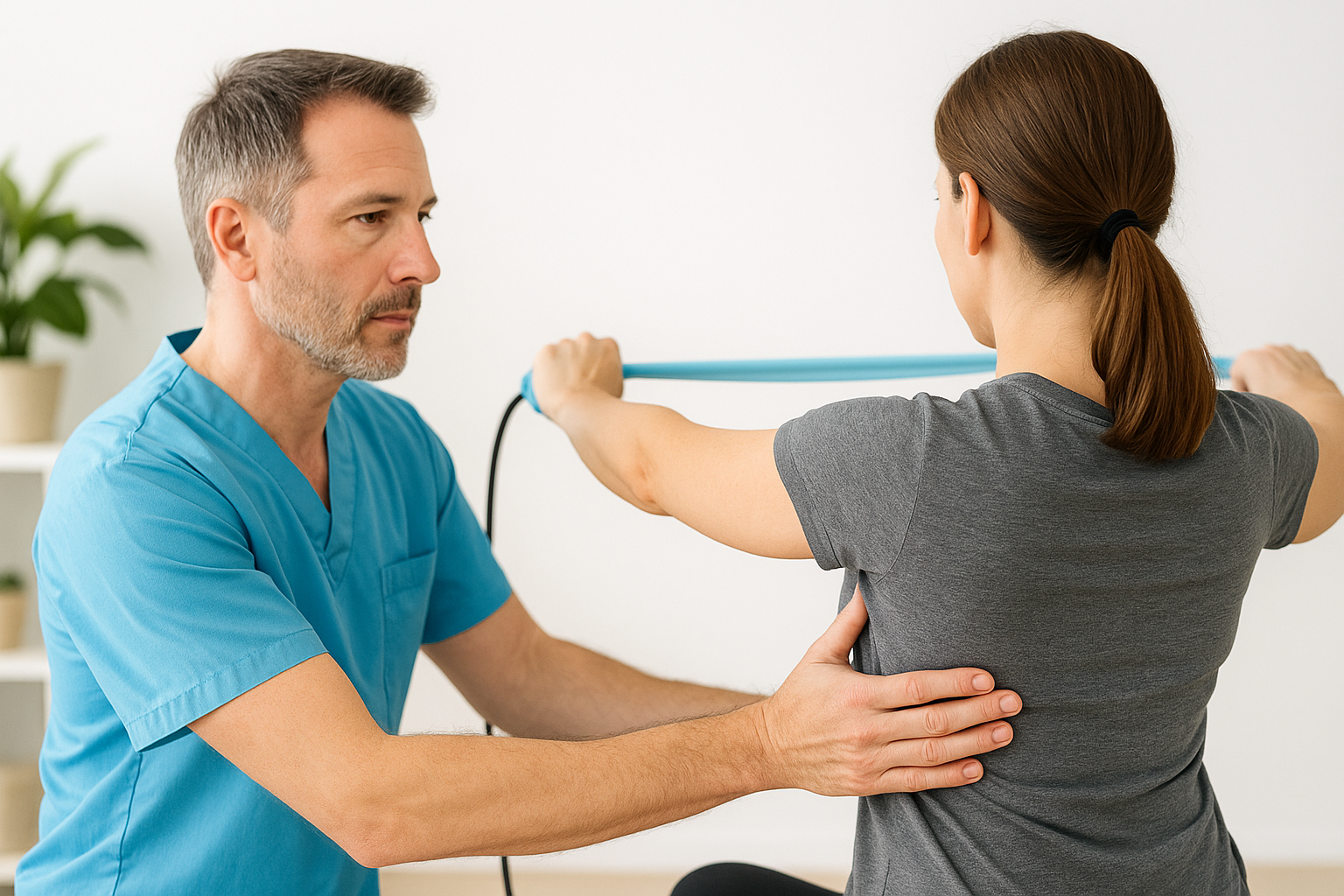
Physiotherapy
Our customized physiotherapy programs use targeted exercises and manual therapy to restore movement, improve strength, and reduce pain, empowering you to regain function and prevent future injuries.

Lifestyle Changes
We guide you in making sustainable lifestyle adjustments, including nutrition, exercise, and stress management, to support your treatment, enhance recovery, and improve your overall quality of life.
How Are We Different from Other Clinics and Orthopedics?
Alleviate Pain Clinic specializes in knee pain treatment without surgery and offers knee pain treatments tailored to individual needs. Our approach includes:

Non-Surgical Pain Treatment
Alleviate Pain Clinic specialises in advanced non-surgical knee pain treatment. Our primary aim is to reduce pain, restore mobility, and eliminate surgery by using evidence-based regenerative medicine, physical therapy, and guided injection with the best shoulder pain specialists who specialise in musculoskeletal care.

Comprehensive Evaluation
Thorough assessments to identify the root cause of knee pain.

Personalized Knee Pain Treatment Plans
Combining physical therapy, medications, and advanced injection therapies.

Expert Team
A multidisciplinary team dedicated to providing compassionate and effective care.
Our Doctors
Reviews
Our Clinics Gallery
Frequently Asked Questions
Multiple factors, including injuries like ligament tears, meniscus damage, or fractures can cause knee joint pain. Chronic conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and bursitis also contribute to knee pain. Overuse, poor posture, obesity, and muscle imbalances can place excessive stress on the knee joint, leading to discomfort. Infections, metabolic conditions like gout, or nerve-related issues can cause knee pain. Diagnosing through imaging and medical evaluation is essential to determine the exact cause and guide treatment.