Arthritis
What is Arthritis?
Arthritis is a term used to describe inflammation of the joints. This inflammation can cause pain, swelling, and reduced motion in the affected joints. While arthritis is commonly associated with older adults, it can affect people of all ages, including children.
The symptoms of arthritis usually develop over time, but they may also appear suddenly. Arthritis is most commonly seen in adults over the age of 65, but it can also develop in children, teens, and younger adults. Arthritis is more common in women than men and in people who are overweight.
Types of Arthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA): The most common type of arthritis, caused by wear and tear on the joints, leading to the breakdown of cartilage.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): An autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system attacks the joints, causing inflammation and joint damage.
Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA): A form of arthritis that affects some people with psoriasis, leading to joint pain and swelling.
Gout: Caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints, resulting in sudden, severe pain and swelling.
Ankylosing Spondylitis: A type of arthritis that primarily affects the spine, causing inflammation and can lead to fusion of the vertebrae.
Juvenile Arthritis: A term used to describe arthritis in children under the age of 16.
The most common among them are Osteoarthritis (OA) and Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA).
Symptoms of Arthritis
Joint Pain: Persistent pain in the joints, often worse with activity.
Stiffness: Reduced range of motion and stiffness, particularly in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
Swelling: Visible swelling in the joints, sometimes accompanied by redness and warmth.
Fatigue: General fatigue and a feeling of being unwell, particularly in autoimmune forms of arthritis.
Decreased Mobility: Difficulty in moving joints freely, affecting daily activities.
Causes of Arthritis
The exact cause of arthritis varies depending on the type. However, several factors can contribute to the development of arthritis:
Genetic Factors: A family history of arthritis can increase the risk of developing the condition.
Age: The risk of many types of arthritis, including osteoarthritis, increases with age.
Gender: Some types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, are more common in women, while others, like gout, are more common in men.
Joint Injuries: Previous joint injuries can lead to arthritis later in life.
Infections: Certain infections can trigger arthritis or make it worse.
Immune System Dysfunction: In autoimmune types of arthritis, such as RA, the immune system mistakenly attacks the joints.
Risk Factors for Arthritis
Obesity: Excess weight can put additional stress on weight-bearing joints, increasing the risk of osteoarthritis.
Occupation: Jobs that require repetitive joint movements or heavy lifting can increase the risk of developing arthritis.
Smoking: Smoking has been linked to the development of rheumatoid arthritis and can exacerbate symptoms.
Diet: Poor nutrition can contribute to inflammation and increase the risk of developing certain types of arthritis, such as gout.
Lack of Physical Activity: A sedentary lifestyle can lead to weak muscles and joints, increasing the risk of arthritis.
Prevention of Arthritis
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Making healthy lifestyle choices can help prevent the onset of arthritis or delay its progression:
Balanced Diet: Eating a nutritious diet to support joint health and overall well-being.
Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity to strengthen muscles and maintain joint flexibility.
Weight Management: Keeping a healthy weight to reduce stress on joints.
Avoiding Joint Injuries
Taking steps to avoid joint injuries can help prevent arthritis:
Protective Gear: Wearing protective gear during sports and high-risk activities.
Proper Technique: Using proper techniques when lifting heavy objects to avoid joint strain.
Safe Environment: Ensuring a safe living and working environment to prevent falls and injuries.
Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection and treatment of arthritis can help manage symptoms and prevent joint damage
FAQs - Knee Osteoarthritis
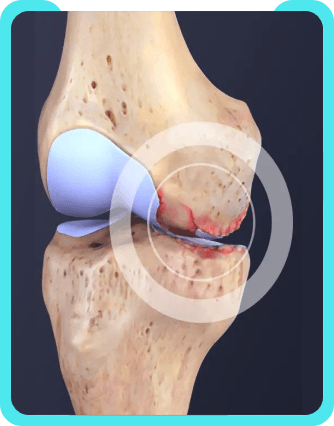
Knee osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint condition where the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of bones in the knee joint wears down over time. This results in pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility in the knee.
Common symptoms include knee pain, stiffness, swelling, reduced range of motion, a grating sensation, and discomfort that worsens with activity and improves with rest.
Diagnosis involves a physical exam, discussing symptoms and medical history, and possibly imaging tests like X-rays to assess the joint’s condition.
Risk factors include age (it’s more common in older adults), family history of osteoarthritis, obesity, previous knee injuries, joint overuse, and gender (more common in women).
Physical therapy includes tailored exercises to strengthen muscles around the knee, improve flexibility, and enhance joint stability. It helps reduce pain, improve function, and enhance overall quality of life.
Regenerative therapies like PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) and stem cell therapy promote natural healing processes by delivering growth factors or stem cells to the affected area. They aid tissue repair, reduce inflammation, and potentially slow down disease progression
PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) therapy involves drawing a small amount of the patient’s blood, processing it to concentrate platelets, and then injecting the PRP into the knee joint. Platelets release growth factors that promote tissue repair, reduce inflammation, and potentially alleviate knee osteoarthritis symptoms.
Stem cell therapy utilizes the body’s own stem cells or those derived from other sources. These cells have the potential to regenerate damaged tissues, promote healing, and reduce inflammation in knee osteoarthritis. Clinical results vary, but research suggests positive outcomes for pain reduction and functional improvement.
Radiofrequency ablation involves using heat to interrupt pain signals from specific nerves. In knee osteoarthritis, genicular nerves are targeted. The procedure can provide effective pain relief and improved joint function, often as part of a comprehensive pain management plan.
Yes, many cases of knee osteoarthritis can be managed without surgery. Non-surgical approaches include medication, physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, injections (corticosteroids, hyaluronic acid, PRP), and regenerative therapies, depending on the severity of the condition.
Lifestyle changes include maintaining a healthy weight to reduce joint stress, engaging in low-impact exercises, avoiding activities that strain the knees, adopting a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, and practicing joint-friendly habits.
Weight management is crucial in knee osteoarthritis as excess weight places added stress on the joints. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces joint strain, decreases pain, and slows down the progression of the condition.
Choosing the right treatment plan involves considering factors like the severity of your condition, lifestyle, preferences, and medical recommendations. Consult with a healthcare professional to create a personalized treatment approach.
Yes, knee osteoarthritis is more common in older adults due to natural wear and tear on the joints over time. However, it can also affect younger individuals, especially those with joint injuries or genetic predisposition.
Yes, home remedies include using hot or cold packs, practicing gentle exercises, maintaining a healthy weight, adopting joint-friendly habits, and trying over-the-counter pain relief methods. Always consult a healthcare professional before trying new remedies.
Untreated knee osteoarthritis can lead to increased pain, reduced joint function, disability, and decreased quality of life. It may also contribute to other joint issues and impact overall mobility.
Gentle and regular exercises focusing on flexibility and strengthening the muscles around the knee can improve joint mobility. Consult a healthcare professional or physical therapist for personalized exercise recommendations.
Yes, genetics can contribute to an increased risk of developing knee osteoarthritis. A family history of the condition may indicate a genetic predisposition, but lifestyle factors also play a significant role.
While high-impact activities may aggravate knee osteoarthritis, low-impact exercises like swimming and cycling can improve joint function and reduce pain. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate activity level.
A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants can help manage knee osteoarthritis. These nutrients support joint health, reduce inflammation, and contribute to overall well-being.
A healthcare professional will assess your condition, considering factors like pain severity, joint damage, response to non-surgical treatments, and overall health. Surgery, such as knee replacement, may be recommended for advanced cases.
Non-surgical treatments offer minimal downtime, reduced risks, and can provide effective pain relief. They include therapies like physical therapy, regenerative treatments, injections, and lifestyle modifications.
Pain medications provide temporary relief, but they don’t address the underlying cause of knee osteoarthritis. Over time, they may have side effects or become less effective. Combining them with other treatments can be more beneficial.
Recovery times vary depending on the treatment type and individual response. Non-surgical treatments may involve minimal downtime, while more invasive procedures like surgery may require weeks to months for full recovery.
During a consultation, a healthcare professional will review your medical history, assess your knee’s condition, discuss symptoms, and recommend diagnostic tests. They will then create a personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs.
No, knee pain can result from various causes, including injuries, strains, and other medical conditions. Accurate diagnosis by a healthcare professional is crucial to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
Yes, knee osteoarthritis can lead to compensatory changes in how you move, potentially affecting other joints like the hips and lower back. Proper treatment and joint-friendly activities can help prevent such effects.
Physical therapy aims to improve joint function, strengthen muscles, and enhance mobility. Customized exercises and techniques taught by a physical therapist can effectively manage knee osteoarthritis symptoms.
Choose low-impact activities like swimming or walking and avoid excessive stress on the knee joint. Consult a healthcare professional or physical therapist for exercise recommendations tailored to your condition.
Knee joint imaging, such as X-rays or MRI scans, provides detailed views of the joint’s structure and any damage. It helps healthcare professionals accurately diagnose knee osteoarthritis and plan appropriate treatments.
Some natural supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin may offer mild relief from knee osteoarthritis symptoms. However, consult a healthcare professional before using supplements, as their effectiveness varies.
Radiofrequency ablation involves using heat to interrupt pain signals from the genicular nerves around the knee joint. By blocking these signals, it provides effective pain relief for knee osteoarthritis without invasive surgery.
Some individuals report that changes in weather conditions, especially cold and damp environments, can worsen knee osteoarthritis symptoms. However, scientific evidence on this connection is inconclusive.
Yes, knee osteoarthritis can affect your ability to perform certain tasks, especially if your job involves physical activities. Proper management, treatments, and accommodations can help mitigate its impact on work.
Multidisciplinary care involves a team of healthcare professionals collaborating to address various aspects of knee osteoarthritis. This approach provides comprehensive and personalized treatment, resulting in improved outcomes.
Knee osteoarthritis can hinder daily activities like walking, climbing stairs, and bending the knee. As the condition progresses, it may limit mobility and impact overall quality of life.
Inflammation is a key factor in knee osteoarthritis progression. It contributes to joint damage and pain. Managing inflammation through treatments and lifestyle changes can help alleviate symptoms.
Severe knee osteoarthritis can impact joint function, leading to limited mobility and affecting daily activities. However, early diagnosis and appropriate management can prevent or minimize disability.
Knee osteoarthritis typically progresses through four stages: mild, moderate, severe, and end-stage. Each stage represents varying degrees of joint degeneration and symptom severity.
Yes, dietary changes can play a role in managing knee osteoarthritis. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, maintaining a healthy weight, and staying hydrated can help alleviate symptoms.
At Alleviate Pain Clinic, we offer customized treatment plans based on individual needs. Our team of specialists assess your condition, medical history, and goals to design a personalized approach for effective knee osteoarthritis management.
Inflammation is a key factor in knee osteoarthritis progression. It contributes to joint damage and pain. Managing inflammation through treatments and lifestyle changes can help alleviate symptoms.
Severe knee osteoarthritis can impact joint function, leading to limited mobility and affecting daily activities. However, early diagnosis and appropriate management can prevent or minimize disability.
Knee osteoarthritis typically progresses through four stages: mild, moderate, severe, and end-stage. Each stage represents varying degrees of joint degeneration and symptom severity.
Yes, dietary changes can play a role in managing knee osteoarthritis. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, maintaining a healthy weight, and staying hydrated can help alleviate symptoms.
At Alleviate Pain Clinic, we offer customized treatment plans based on individual needs. Our team of specialists assess your condition, medical history, and goals to design a personalized approach for effective knee osteoarthritis management.
Advanced treatments offer more precise targeting, quicker recovery, reduced risk of complications, and often avoid the need for invasive surgeries. They can address the underlying cause and provide longer-lasting relief.
At Alleviate Pain Clinic, patient comfort is paramount. We use advanced techniques, offer sedation options, and ensure open communication to create a supportive environment during treatments.
Insurance coverage for knee osteoarthritis treatment varies based on individual plans. Alleviate Pain Clinic collaborates with multiple insurance providers to help patients navigate their coverage options.
To prepare for your first appointment, gather your medical history, relevant test reports, and a list of current medications. Be ready to discuss your symptoms, concerns, and treatment goals in detail.
While more common in older adults, knee osteoarthritis can affect young adults due to factors like genetics, injuries, or overuse. Early diagnosis and tailored treatment plans are essential for young patients.
Yes, Alleviate Pain Clinic offers innovative therapies such as regenerative treatments, advanced injections, and cutting-edge techniques that provide effective relief and promote healing.
Alleviate Pain Clinic differentiates itself with its comprehensive approach, specialized team of experts, utilization of the latest technologies, personalized treatment plans, and a commitment to enhancing patients’ quality of life.
Video Spotlight
Blog
Surgery-Free Solutions
Expert Tips for Pain Management
Testimonials
Words From Our Patients
The treatment was very good and the doctor Faraz Ahmed was very kind to the patient and explained clearly the procedure of knee bilateral ha & treatment And we were advised to do physiotherapy. We are very much satisfied. We would recommend this alleviate pain clinic. Thank you
Got treatment of Treatment and HA for right knee arthritis a month ago and finding good relief from pain. Was treated by Dr Swagtesh Bastia who explained very well about the injections and the treatment was painless. The front desk staff were very kind and very helpful and physiotherapy was also done expertly, overall good experience
Alleviate Pain Management clinic has been a godsend for my mom's knee pain. She has been treated by Dr. Wiquar Ahmed. The attentive staff provided personalised care, and after her treatment, she's feeling remarkably better. Thank you for giving my mom the relief she deserves!
The clinic is super clean with a great OT and most importantly all the staff here are very helpful and considerate. My gratitude to Dr Roshan, the nurses, and support staff - they were always available to assist with any issues post procedure and they even made an extra effort to make a home visit for a follow up check-up. This team here is the perfect example of healing and care with a human touch. Thank you!!!!!
My wife had knee pain I have visited alleviate pain and consulted doc santhoshi now she is able to walk pain free and can do her daily activity than before.the physiotherapist here Dr akhila also helped her with few exercises and the staff here Abdul explained all the procedures well . Thank you PPL can visit here for pain relief