Knee Tendonitis
- Home
- Conditions
- Knee pain
- Knee Tendonitis
What is Knee Tendonitis?
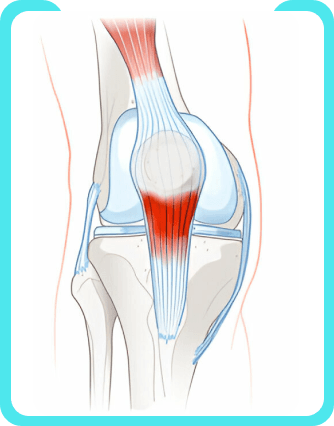
Patellar tendonitis is a common injury or inflammation of the tendon that connects your kneecap (patella) to your shinbone (tibia). Your pain may be mild or severe.
Anyone can get patellar tendonitis. But it’s such a frequent injury of athletes, especially those who play volleyball and basketball, that it’s called jumper’s knee.
Patellar tendonitis comes from repetitive stress on the knee, most often from overuse in sports or exercise. The repetitive stress on the knee creates tiny tears in the tendon that, over time, inflame and weaken the tendon.
Treatment for Knee Tendonitis

FAQ'S
- tight leg muscles
- uneven leg muscle strength
- misaligned feet, ankles, and legs
- obesity
- shoes without enough padding
- hard playing surfaces
- chronic diseases that weaken the tendon
Athletes are more at risk because running, jumping, and squatting put more force on the patellar tendon. For example, running can put a force of up to five times your body weight on your knees.
Pain and tenderness at the base of your kneecap are usually the first symptoms of patellar tendonitis. You may also have some swelling and a burning feeling in the kneecap. Kneeling down or getting up from a squat can be especially painful.
The pain may at first be sporadic, occurring only after sports or exercise activity. As the tendon becomes more damaged, the pain can become progressively worse. It can interfere with any athletic activity, as well as with daily activities, such as climbing stairs or sitting in a car.
The first step in treating Knee Tendonitis is to make an appointment to see a doctor who specializes in Sports Medicine and knee injuries for a diagnosis and to learn your treatment options.
Treatment for Knee Tendonitis varies greatly depending on the severity of the inflammation. For mild cases of Jumper’s Knee, simple methods such as the RICE Method: Rest, Ice, Compression and Elevation, may be recommended. For moderate to severe cases of Jumper’s Knee treatment may include may include anti-inflammatory medication, Physical Therapy, Rehabilitation programs and Injections for Pain Management.
At Alleviate, personalized treatment plans for knee injuries or sports injuries are designed for each individual patient by our expert staff.
Video Spotlight
Blog
Surgery-Free Solutions
Expert Tips for Pain Management
Testimonials
Words From Our Patients
The treatment was very good and the doctor Faraz Ahmed was very kind to the patient and explained clearly the procedure of knee bilateral ha & treatment And we were advised to do physiotherapy. We are very much satisfied. We would recommend this alleviate pain clinic. Thank you
Got treatment of Treatment and HA for right knee arthritis a month ago and finding good relief from pain. Was treated by Dr Swagtesh Bastia who explained very well about the injections and the treatment was painless. The front desk staff were very kind and very helpful and physiotherapy was also done expertly, overall good experience
Alleviate Pain Management clinic has been a godsend for my mom's knee pain. She has been treated by Dr. Wiquar Ahmed. The attentive staff provided personalised care, and after her treatment, she's feeling remarkably better. Thank you for giving my mom the relief she deserves!
The clinic is super clean with a great OT and most importantly all the staff here are very helpful and considerate. My gratitude to Dr Roshan, the nurses, and support staff - they were always available to assist with any issues post procedure and they even made an extra effort to make a home visit for a follow up check-up. This team here is the perfect example of healing and care with a human touch. Thank you!!!!!
My wife had knee pain I have visited alleviate pain and consulted doc santhoshi now she is able to walk pain free and can do her daily activity than before.the physiotherapist here Dr akhila also helped her with few exercises and the staff here Abdul explained all the procedures well . Thank you PPL can visit here for pain relief