

Tennis Elbow
- Home
- Conditions
- Elbow Pain
- Tennis Elbow
Tennis elbow or lateral epicondylitis is a condition which brings about pain and discomfort on the outer side of the elbow. This is the part of the elbow where the extensor muscles of the forearm originate from humerus (bone) through a common extensor origin. The most commonly involved tendon is Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis. Usually degeneration is noticed at the attachment of the tendon on the bone.Weakening of the attachment leads to greater stress in the area as there is a compromise on the tendon’s bony anchor point. Sports such as tennis or other activities requiring repetitive gripping, grasping or lifting activities are the usual culprits in the progression of tennis elbow.
Preponderance- It is commonly seen in the age groups of 30-50 and
relatively equal incidence in both gender groups.
Etiology/Causes of Tennis Elbow
Any activity leading to overuse of the extensor tendons of the forearm especially with the palm facing down can predispose an individual to micro tears and inflammation characteristic of Lateral epicondylitis/tennis elbow.
Some of these activities include:
- Constant gripping tasks riding a two wheeler , athletic activities like tennis or pushing or carrying heavy loads.
- Activities such as typing and use of tools on a daily basis bringing about repetitive load on the extensor muscles.
- Trauma resulting from a direct impact or blow to the elbow can cause inflammation of the tendon leading to degeneration.
Symptoms
Pain on the outer aspect of the elbow is the most pressing symptom. The bony point of tenderness is over the lateral epicondyle. Pain is aggravated by movements involving gripping, pushing and grasping. Patient may complain of pain limited to the lateral epicondyle but in some cases patients can be seen experiencing radiating pain down to the forearm.


Signs
Purpose of these tests is to maximally stretch and provoke the muscles of Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus and extensor carpi Radialis Brevis.
- Mill’s test – Standing position Bring the forearm is pronated and brought to full extension, palm facing back , palpate the lateral Epicondyle.
- Cozen’s test – Sitting position, forearm pronated, elbow extended, ask the patient to extend their wrist against resistance. Pain over the Lateral Epicondyle.
Diagnosis
Usually History and Clinical examination are very suggestive but diagnosis can be confirmed by imaging such as Ultrasound or MRI of the elbow.


Signs
Conservative approaches include limitation of offending activity like typing or gripping.
- Patients can be offered anti inflammatory medications.
- Tennis elbow splints/ braces are useful in reducing the strain on the elbow extensors.
- Physical therapy involving manual massage, ice massage and modalities like Ultrasound can be used to soothen the symptoms of lateral epicondylitis
- Taping of the affected elbow can be tried in conjunction with these other approaches.
- Lifestyle modification include limitation of offending activity like typing and gripping.
Exercise Protocol for Tennis Elbow
Stretching and strengthening of the affected muscle groups forms a very important part of the rehabilitation regime. Exercises broadly include


Forearm
extensor stretch


Eccentric wrist
extensors strengthening
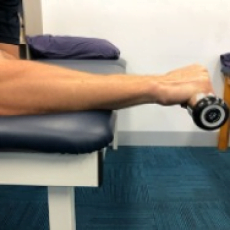

Isometric wrist
extensor strengthening


Isotonic wrist
extensor strengthening
Treatment at Alleviate
- Anti-Inflammatory injection – Corticosteroids can be injected blind or with image guidance on the inflamed surface to help relieve the inflammation so that the patient can start rehabilitation. Care should be taken not to give successive steroid injections at the same site
- Platelet Rich Plasma with Prolotherapy – Treatment with Ultrasound guided Platelet Rich Plasma with Prolotherapy is an excellent treatment option as it brings about healing of the damaged tendon. Generally 2-3 sittings of Prp with prolotherapy coupled with regular exercises has been seen to be very effective in controlling the troublesome symptoms of tennis elbow.
- Stem Cells – Stem Cell injection into the damaged tendon has been tried for some chronic cases.
- Surgery – Arthroscopic or open surgery can be used to remove the degenerated tendon in chronic, resistant cases not responding to non operative means.
FAQs - Tennis Elbow
Tennis elbow or lateral epicondylitis is a condition in which the outer side of the elbow will have pain and discomfort. The area between the elbow joint and the wrist (forearm) is usually degenerated and overused.
- The major cause of lateral epicondylitis is due to overuse.
- Any activity that involves stress in the tendon, the extensor muscles of the forearm can cause the disorder.
- People who are involved in the occupation of the repetitive motions of the wrist and arms.
- Sports related activities such as tennis, golf, or other activities like repetitive work, lifting, or gardening are usually the victims in the progression of the tennis elbow.
Following are the activities that a person can tennis elbow:
- Tasks involving constant gripping such as riding a two-wheeler, sports or athletic activities like tennis, carrying or pushing heavy weights.
- Occupation involving typing and use of tools
- It can also affect due to trauma resulting in the direct impact to the elbow, which can cause inflammation resulting in degenerating tendon.
It is commonly seen in the age groups of 30-50 in both gender groups.
Lateral epicondylitis gets worsens if not treated. It can lead to serious problems like loss of motion or function of the elbow and forearm. Even it can lessen the grip as the condition worsens.
The symptoms involving tennis elbow or lateral epicondylitis include:
- Pain on the outer area of the elbow
- Tenderness in the bony point over the lateral epicondyle
- Pain can be aggravated by movements
- Pain is limited to the lateral epicondyle but can radiate to the forearm in some cases.
In most cases, non-surgical therapies yield a high success rate. Treatments involve for tennis elbow/lateral epicondylitis are:
- Conservative Treatment
- Exercise
- Surgery
Anti-inflammatory Medications are offered to the patient. Tennis elbow splints or braces are used to reduce the strain on the elbow extensors.
Patient suffering from tennis elbow can get physical therapy sessions from an experienced physical therapist. It involves:
- Manual Massage
- Ice Massage
- Ultrasound to stimulate healing and soothing effect
Yes, taping can be done for the affected elbow in conjunction with other treatment approaches.
Limitation of offending activity like typing and gripping.
Yes, it helps. Stretching and strengthening of the affective muscle groups help in the rehabilitation regime. Below are the exercises involving stretching and strengthening:
- Forearm extensor stretch
- Eccentric wrist extensors strengthening
- Isometric wrist extensor strengthening
- Isotonic wrist extensor strengthening
Corticosteroids are injected to help relieve the inflammation and the patient starts the rehabilitation process.
Treatment with Ultrasound guided Platelet Rich Plasma with Prolotherapy is an excellent procedure that elevates the healing process of the damaged tendon. Usually, 2 to 3 sittings of PRP with Prolotherapy are required. PRP treatment can be combined with regular exercise.
Stem cell injection can be tried for some chronic cases by injecting into the damaged tendon.
Arthroscopic or open surgery can be sued to remove degenerated tendons in chronic, cases not responding to the non-operative means.
Video Spotlight
Blog
Surgery-Free Solutions
Expert Tips for Pain Management
Testimonials
Words From Our Patients
The treatment was very good and the doctor Faraz Ahmed was very kind to the patient and explained clearly the procedure of knee bilateral ha & botox And we were advised to do physiotherapy. We are very much satisfied. We would recommend this alleviate pain clinic.Thank you
Got treatment of Botox and HA for right knee arthritis a month ago and finding good relief from pain. Was treated by Dr Swagtesh Bastia who explained very well about the injections and the treatment was painless. The front desk staff were very kind and very helpful and physiotherapy was also done expertly, overall good experience
Alleviate Pain Management clinic has been a godsend for my mom's knee pain. She has been treated by Dr. Wiquar Ahmed. The attentive staff provided personalised care, and after her treatment, she's feeling remarkably better. Thank you for giving my mom the relief she deserves!
The clinic is super clean with a great OT and most importantly all the staff here are very helpful and considerate. My gratitude to Dr Roshan, the nurses, and support staff - they were always available to assist with any issues post procedure and they even made an extra effort to make a home visit for a follow up check-up. This team here is the perfect example of healing and care with a human touch. Thank you!!!!!
My wife had knee pain I have visited alleviate pain and consulted doc santhoshi now she is able to walk pain free and can do her daily activity than before.the physiotherapist here Dr akhila also helped her with few exercises and the staff here Abdul explained all the procedures well . Thank you PPL can visit here for pain relief





