Introduction
Chronic lower back pain can significantly impact daily life, often requiring effective pain management strategies. Lumbar Epidural Steroid Injection (LESI) has gained prominence as a targeted approach to provide relief from pain caused by various spinal conditions. In this blog, we’ll delve into the clinical results and efficacy of LESIs, identify the candidates who can benefit from this procedure, and set realistic expectations for those considering it.Indications for Lumbar Epidural Steroid Injections
Lumbar epidural steroid injections are recommended for a range of spinal conditions, including- Lumbar Radiculopathy : LESIs are commonly used to manage radiating nerve pain caused by compressed or irritated spinal nerves, often due to herniated discs or spinal stenosis.
- Spinal Stenosis : Patients with spinal stenosis, characterized by narrowing of the spinal canal, can experience relief from LESIs as they target the inflammation contributing to pain.
- Degenerative Disc Disease : LESIs can be beneficial in managing chronic lower back pain stemming from degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs.
- Post-Surgery Pain : In some cases, patients who continue to experience pain after spine surgery might benefit from LESIs to mitigate inflammation and pain.
Types of Lumbar Epidural Steroid Injections
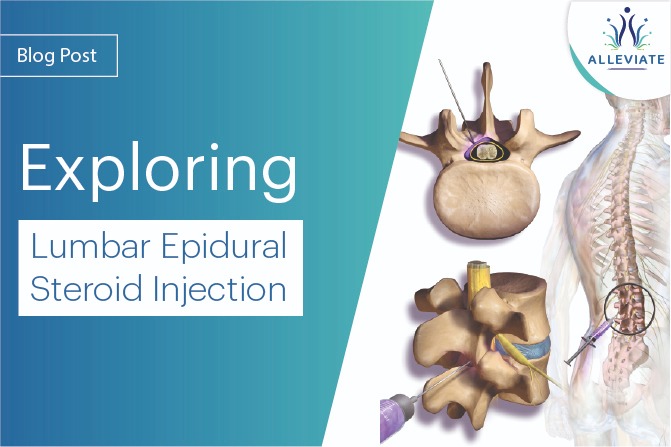
- Interlaminar Epidural Injection : This technique involves injecting the steroid medication into the epidural space through the ligamentum flavum, between adjacent vertebrae. It aims to target inflammation around the spinal nerves.
- Transforaminal Epidural Injection : In this approach, the injection is administered into the neural foramen, targeting the area where the spinal nerve exits the spine. This technique offers more specific nerve root coverage.
Mechanism of Action of Lumbar Epidural Steroid Injections
The precise mechanism of action of LESIs involves various components- Anti-Inflammatory Effects : Steroids have potent anti-inflammatory properties. When injected into the epidural space, they can suppress inflammation around spinal nerves, reducing pain and irritation.
- Pain Modulation : Steroids can influence the transmission of pain signals by inhibiting the release of certain neurotransmitters and reducing nerve sensitivity.
- Edema Reduction : LESIs can help reduce swelling and edema around inflamed spinal nerves, contributing to pain relief.
- Promotion of Healing : Steroids can facilitate the healing process by minimizing inflammation, allowing damaged tissues to recover more effectively.
Conclusion : Embracing Effective Pain Management
Lumbar epidural steroid injections have emerged as a valuable tool in managing various spinal conditions causing pain and discomfort. By understanding the indications for LESIs, the different types available, and the intricate mechanism of action, patients and healthcare providers can make informed decisions about the most appropriate pain management strategies. As with any medical procedure, consultation with a qualified healthcare professional is essential to determine the suitability of LESIs and ensure a comprehensive and personalized approach to pain relief.Efficacy of Lumbar Epidural Steroid Injections
Clinical studies have highlighted the positive impact of LESIs on pain relief and quality of life:- A study published in the Journal of Spinal Disorders & Techniques demonstrated that LESIs resulted in significant pain reduction and improved functional outcomes in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis
- Another research article in the Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery found that LESIs effectively relieved radicular pain caused by disc herniation, with improvement reported by over 75% of the patients
- The Journal of Clinical Anesthesia published a study indicating that LESIs provided considerable pain relief and reduced disability in patients suffering from lumbar degenerative disc disease
Candidates for Lumbar Epidural Steroid Injections :
LESI is recommended for individuals who meet certain criteria:- Radiculopathy or Nerve Compression : Patients experiencing radiating nerve pain due to conditions like herniated discs or spinal stenosis are prime candidates for LESIs
- Failed Conservative Treatments : Individuals who have not experienced significant relief from conservative treatments like medications, physical therapy, and rest might find LESIs beneficial
- Functional Impairment : Patients whose pain significantly impacts their daily activities and quality of life can consider LESIs as an option for managing pain
What Can You Expect from the Procedure?
- Pre-Procedure Evaluation : Your healthcare provider will conduct a thorough assessment, review your medical history, and possibly order imaging tests to confirm the source of your pain and determine the suitability of LESIs.
- During the Procedure : LESIs are performed on an outpatient basis. The procedure involves injecting a combination of anesthetic and steroid medication into the epidural space around the affected nerve root. Fluoroscopy or ultrasound guidance ensures accurate needle placement.
- Immediate Effects : While some patients may experience immediate pain relief due to the local anesthetic, the steroid medication’s anti-inflammatory effects can take a few days to fully manifest.
- Post-Procedure Care : You may be advised to rest for a short period after the procedure and gradually resume activities. Follow-up appointments will allow your healthcare provider to assess your response to the injection
Conclusion: Navigating Lumbar Epidural Steroid Injections
Lumbar Epidural Steroid Injections offer a well-established approach to managing chronic lower back pain arising from various spinal conditions. With compelling clinical results and demonstrated efficacy, they provide hope for individuals seeking relief from persistent pain. By identifying suitable candidates and understanding the procedural expectations, patients can make informed decisions in consultation with their healthcare providers. As with any medical procedure, open communication and collaboration between patients and medical professionals are key to achieving the best possible outcomes.References
- Lee BH, Moon SH, Suk KS, Kim HS, Yang JH, Lee HM. Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: Pathophysiology and Treatment Principle: A Narrative Review. Asian Spine J. 2020 Oct;14(5):682-693. doi: 10.31616/asj.2020.0472. Epub 2020 Oct 14. PMID: 33108834; PMCID: PMC7595829.
- Raja A, Hoang S, Patel P, et al. Spinal Stenosis. [Updated 2023 Jun 12]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441989/
- Donnally III CJ, Hanna A, Varacallo M. Lumbar Degenerative Disk Disease. [Updated 2023 Aug 4]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448134/
- Bajwa SJ, Haldar R. Pain management following spinal surgeries: An appraisal of the available options. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2015 Jul-Sep;6(3):105-10. doi: 10.4103/0974-8237.161589. PMID: 26288544; PMCID: PMC4530508.
- Hakim BR, Munakomi S. Interlaminar Epidural Injection. [Updated 2023 Aug 13]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545197/
- The Lumbar Neural Foramen and Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injections: An Anatomic Review With Key Safety Considerations in Planning the Percutaneous ApproachAuthors: Jacob C. Mandell, Gregory J. Czuczman, Glenn C. Gaviola, Varand Ghazikhanian, and Charles H. ChoAUTHOR INFO & AFFILIATIONSVolume 209, Issue https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.16.17471
- Lee BH, Moon SH, Suk KS, Kim HS, Yang JH, Lee HM. Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: Pathophysiology and Treatment Principle: A Narrative Review. Asian Spine J. 2020 Oct;14(5):682-693. doi: 10.31616/asj.2020.0472. Epub 2020 Oct 14. PMID: 33108834; PMCID: PMC7595829.
- Jordan J, Konstantinou K, O’Dowd J. Herniated lumbar disc. BMJ Clin Evid. 2011 Jun 28;2011:1118. PMID: 21711958; PMCID: PMC3275148.
- Sayed D, Grider J, Strand N, Hagedorn JM, Falowski S, Lam CM, Tieppo Francio V, Beall DP, Tomycz ND, Davanzo JR, Aiyer R, Lee DW, Kalia H, Sheen S, Malinowski MN, Verdolin M, Vodapally S, Carayannopoulos A, Jain S, Azeem N, Tolba R, Chang Chien GC, Ghosh P, Mazzola AJ, Amirdelfan K, Chakravarthy K, Petersen E, Schatman ME, Deer T. The American Society of Pain and Neuroscience (ASPN) Evidence-Based Clinical Guideline of Interventional Treatments for Low Back Pain. J Pain Res. 2022 Dec 6;15:3729-3832. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S386879. Erratum in: J Pain Res. 2022 Dec 24;15:4075-4076. PMID: 36510616; PMCID: PMC9739111.
- Dydyk AM, Conermann T. Chronic Pain. [Updated 2023 Jul 21]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553030/
- Committee on Diagnostic Error in Health Care; Board on Health Care Services; Institute of Medicine; The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Balogh EP, Miller BT, Ball JR, editors. Improving Diagnosis in Health Care. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2015 Dec 29. 2, The Diagnostic Process. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK338593/
- Park KD, Kim TK, Lee WY, Ahn J, Koh SH, Park Y. Ultrasound-Guided Versus Fluoroscopy-Guided Caudal Epidural Steroid Injection for the Treatment of Unilateral Lower Lumbar Radicular Pain: Case-Controlled, Retrospective, Comparative Study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015 Dec;94(50):e2261. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002261. PMID: 26683948; PMCID: PMC5058920