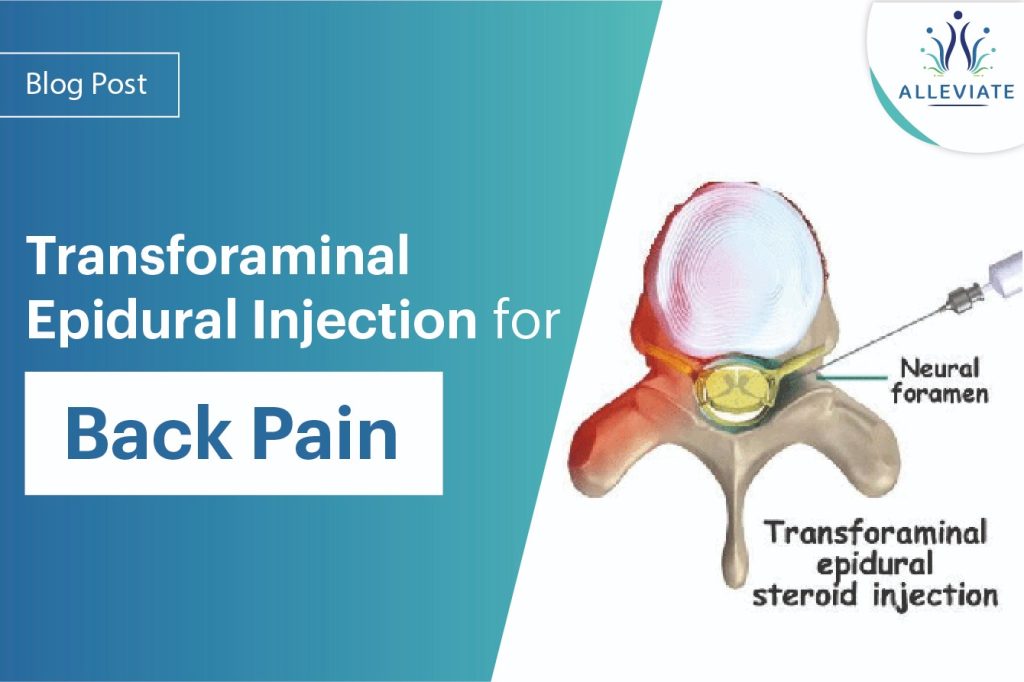
Introduction
Back pain is a common ailment that can significantly impact one’s quality of life. Transforaminal Epidural Injections (TFEIs) have emerged as a targeted and effective pain management technique for various spinal conditions. In this blog, we will delve into the indications for TFEIs, explore the different approaches used in the procedure, and examine the clinical results and efficacy backed by insights from published articles and medical journals.
Indications for Transforaminal Epidural Injections
TFEIs are recommended for a range of spinal conditions, including:Lumbar Radiculopathy : TFEIs are commonly used to alleviate radiculopathy caused by nerve compression due to herniated discs or spinal stenosis.
Spinal Stenosis : Patients with spinal stenosis, characterized by the narrowing of the spinal canal, can benefit from TFEIs as they target the inflammation contributing to pain.
Discogenic Pain : Individuals with discogenic pain, often due to degenerative disc disease, can experience relief from TFEIs that target the affected nerve roots.
Facet Joint Arthritis : TFEIs can provide relief for pain arising from facet joint arthritis, particularly when combined with diagnostic blocks to pinpoint the source of pain .
Techniques for Transforaminal Epidural Injections
Infrapedicular Approach:This approach involves inserting the needle below the pedicle, aiming to target the spinal nerve root. It’s often used when the safe triangle approach is not feasible due to anatomical variations .
Safe Triangle Approach:The safe triangle approach targets the superior articular process, the pedicle, and the traversing nerve root. It ensures safe and accurate needle placement while minimizing the risk of complications.
Kambin’s Triangle Approach:Kambin’s Triangle approach involves inserting the needle through the intervertebral foramen, between the exiting and traversing nerve roots. It offers direct access to the epidural space, effectively delivering medication to the target area.Infrapedicular Approach:This approach involves inserting the needle below the pedicle, aiming to target the spinal nerve root. It’s often used when the safe triangle approach is not feasible due to anatomical variations.
Safe Triangle Approach:The safe triangle approach targets the superior articular process, the pedicle, and the traversing nerve root. It ensures safe and accurate needle placement while minimizing the risk of complications.
Kambin’s Triangle Approach:Kambin’s Triangle approach involves inserting the needle through the intervertebral foramen, between the exiting and traversing nerve roots. It offers direct access to the epidural space, effectively delivering medication to the target area.
Clinical Results and Efficacy
Pain Reduction and Improved Functionality : A study published in the Journal of Pain Research reported that TFEIs provided significant pain reduction and improved functionality in patients with lumbar radiculopathy .
Superior Pain Relief in Comparison Studies : Comparative studies have demonstrated the superiority of TFEIs in pain relief. A randomized controlled trial published in the European Spine Journal found TFEIs to be more effective than transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for lumbar radiculopathy.
Long-Term Benefits : Research published in the Pain Physician journal highlighted the long-term benefits of TFEIs, with pain relief lasting up to six months or more in some patients .
Positive Impact on Quality of Life : A study in the Journal of Spinal Disorders & Techniques revealed that TFEIs not only reduced pain but also significantly improved patients’ quality of life and overall well-being.
Fluroscopy Guided Transforaminal Epidural Injection




Conclusion : Harnessing the Power of Transforaminal Epidural Injections
Transforaminal Epidural Injections offer a focused and effective approach to managing back pain stemming from various spinal conditions. By understanding the indications for TFEIs, the different techniques used for precise needle placement, and the compelling clinical results demonstrating their efficacy, patients and healthcare providers can make informed decisions about pain management strategies. As with any medical procedure, consultation with a qualified healthcare professional is crucial to determine the most suitable treatment plan tailored to individual needs. TFEIs provide hope for those seeking targeted relief, helping them embark on a journey towards improved comfort and quality of life.
References
- Berry JA, Elia C, Saini HS, Miulli DE. A Review of Lumbar Radiculopathy, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Cureus. 2019 Oct 17;11(10):e5934. doi: 10.7759/cureus.5934. PMID: 31788391; PMCID: PMC6858271.
- Raja A, Hoang S, Patel P, et al. Spinal Stenosis. [Updated 2023 Jun 12]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441989/
- Fujii K, Yamazaki M, Kang JD, Risbud MV, Cho SK, Qureshi SA, Hecht AC, Iatridis JC. Discogenic Back Pain: Literature Review of Definition, Diagnosis, and Treatment. JBMR Plus. 2019 Mar 4;3(5):e10180. doi: 10.1002/jbm4.10180. PMID: 31131347; PMCID: PMC6524679.
- Perolat R, Kastler A, Nicot B, Pellat JM, Tahon F, Attye A, Heck O, Boubagra K, Grand S, Krainik A. Facet joint syndrome: from diagnosis to interventional management. Insights Imaging. 2018 Oct;9(5):773-789. doi: 10.1007/s13244-018-0638-x. Epub 2018 Aug 8. PMID: 30090998; PMCID: PMC6206372.
- Gil HY, Jeong S, Cho H, Choi E, Nahm FS, Lee PB. Kambin’s Triangle Approach versus Traditional Safe Triangle Approach for Percutaneous Transforaminal Epidural Adhesiolysis Using an Inflatable Balloon Catheter: A Pilot Study. J Clin Med. 2019 Nov 15;8(11):1996. doi: 10.3390/jcm8111996. PMID: 31731783; PMCID: PMC6912526.
- Park JW, Nam HS, Cho SK, Jung HJ, Lee BJ, Park Y. Kambin’s Triangle Approach of Lumbar Transforaminal Epidural Injection with Spinal Stenosis. Ann Rehabil Med. 2011 Dec;35(6):833-43. doi: 10.5535/arm.2011.35.6.833. Epub 2011 Dec 30. PMID: 22506212; PMCID: PMC3309379.
- Lee J, Jo D, Song S, Park D, Kim D, Oh J. Effect of Needle Tip Position on Contrast Media Dispersion Pattern in Transforaminal Epidural Injection Using Kambin’s Triangle Approach. J Pain Res. 2020 Nov 10;13:2869-2878. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S270450. PMID: 33204148; PMCID: PMC7667514.
- Treatment of Chronic Lumbosacral Radicular Pain Using AdjuvantPulsedRadiofrequency: A Randomized Controlled Study Wonuk Koh, MD, PhD, Seong-Soo Choi, MD, PhD, Myong Hwan Karm, MD, Jeong Hun Suh, MD, PhD, Jeong Gil Leem, MD, PhD, Jae Do Lee, MD, Young Ki Kim, MD, PhD, Jinwoo Shin, MD, PhD Pain Medicine, Volume 16, Issue 3, March 2015, Pages 432–441, https://doi.org/10.1111/pme.12624
- Kennedy DJ, Plastaras C, Casey E, Visco CJ, Rittenberg JD, Conrad B, Sigler J, Dreyfuss P. Comparative effectiveness of lumbar transforaminal epidural steroid injections with particulate versus nonparticulate corticosteroids for lumbar radicular pain due to intervertebral disc herniation: a prospective, randomized, double-blind trial. Pain Med. 2014 Apr;15(4):548-55. doi: 10.1111/pme.12325. Epub 2014 Jan 2. PMID: 24393129.
- Koh WU, Choi SS, Park SY, Joo EY, Kim SH, Lee JD, Shin JY, Suh JH, Leem JG, Shin JW. Transforaminal hypertonic saline for the treatment of lumbar lateral canal stenosis: a double-blinded, randomized, active-control trial. Pain Physician. 2013 May-Jun;16(3):197-211. PMID: 23703407.
- Manca A, Kumar K, Taylor RS, Jacques L, Eldabe S, Meglio M, Molet J, Thomson S, O’Callaghan J, Eisenberg E, Milbouw G, Buchser E, Fortini G, Richardson J, Taylor RJ, Goeree R, Sculpher MJ. Quality of life, resource consumption and costs of spinal cord stimulation versus conventional medical management in neuropathic pain patients with failed back surgery syndrome (PROCESS trial). Eur J Pain. 2008 Nov;12(8):1047-58. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpain.2008.01.014. Epub 2008 Mar 21. PMID: 18359255.