Introduction
Neck pain can be a debilitating issue that affects a significant portion of the population. It can manifest on one side of the neck, such as right-sided neck pain, and be attributed to various underlying factors. In this blog, we will explore 12 common causes of right-sided neck pain, with a particular focus on muscular strain/sprain, trigger points, cervical facet joint pain, cervical radiculopathy, cervical instability/whiplash injury, poor ergonomics, cervical disc degenerative disease, cervicogenic headaches, lymph node enlargement, brachial plexus injury, anxiety/stress, and benign or malignant growth.
Muscular Strain/Sprain
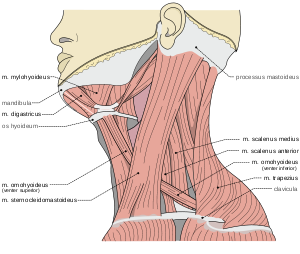
Anatomy of muscles in the neck. Sternocleidomastoid is very commonly affected with strains and sprains resulting in TorticollisMuscular strain or sprain in the neck is one of the most common causes of right-sided neck pain. Overuse, poor posture, or sudden movements can lead to muscle tension and discomfort. It’s essential to maintain proper posture and engage in regular neck exercises to prevent these issues.(
Trigger Points

Trigger points are localized knots in the muscles that can cause referred pain in the neck. These points often require manual therapy or trigger point injections for relief.
Cervical Facet Joint Arthritis

The facet joints in the cervical spine can become inflamed or degenerate, leading to neck pain. This pain can be felt on one side of the neck and may be exacerbated by certain movements.
Cervical Radiculopathy

Cervical radiculopathy occurs when nerves in the neck are compressed or irritated, often due to herniated discs. This condition can lead to sharp, shooting pains on one side of the neck.
Cervical Instability/Whiplash Injury

Whiplash injuries, often caused by car accidents, can result in neck pain due to cervical instability. The abrupt back-and-forth movement can damage ligaments and soft tissues in the neck.
Poor Ergonomics

Prolonged poor posture and ergonomic practices, such as working at a computer with an improperly positioned screen or keyboard, can lead to neck pain. Adjusting your workspace and practicing good ergonomics is crucial in preventing this.
Cervical Disc Degenerative Disease

As we age, the discs in our neck can degenerate, leading to chronic neck pain. This degeneration can cause stiffness, limited mobility, and radiating pain into the arm.
Cervicogenic Headaches
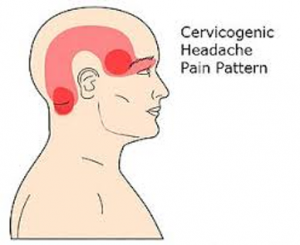
Cervicogenic headaches are a type of headache that originates from the neck. This condition can lead to pain on one side of the neck and may be accompanied by headache symptoms.
Lymph Node Enlargement

Swollen lymph node in the neck due to tick attached behind earEnlarged lymph nodes in the neck, often due to infections, can cause localized neck pain. It’s important to address the underlying cause of lymph node enlargement for effective treatment.
Brachial Plexus Injury
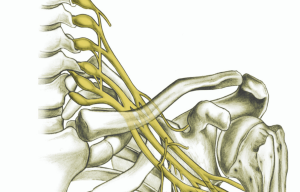
Injuries to the brachial plexus, a network of nerves that control arm and hand movements, can result in neck pain. This type of pain often radiates from the neck into the arm.
Anxiety/Stress

Psychological factors such as anxiety and stress can lead to muscle tension and pain in the neck. Relaxation techniques, stress management, and therapy can be effective in reducing neck pain caused by these factors.
Benign or Malignant Growth

In some cases, neck pain on one side may be caused by a benign or malignant growth, such as a tumor or cyst. Early diagnosis and appropriate medical intervention are crucial in these instances.
Conclusion
Right-sided neck pain can be attributed to various causes, ranging from muscular strain to underlying medical conditions. Proper diagnosis and targeted treatment, often guided by a healthcare professional, are essential for effective pain management and improved quality of life. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider such as Alleviate Pain Clinic, if you experience persistent or severe neck pain to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate care.
References
- Ma G, Dou Y, Dang S, Yu N, Guo Y, Yang C, Lu S, Han D, Jin C. Influence of Monoenergetic Images at Different Energy Levels in Dual-Energy Spectral CT on the Accuracy of Computer-Aided Detection for Pulmonary Embolism. Acad Radiol. 2019 Jul;26(7):967-973. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2018.09.007. Epub 2019 Feb 22. PMID: 30803897.
- Touma J, May T, Isaacson AC. Cervical Myofascial Pain. [Updated 2023 Jul 3]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507825/
- Su DCJ, Chang KV. Facet Arthritis. [Updated 2023 Jul 4]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493233/
- Factors associated with chronic opioid use after cervical spine surgery for degenerative conditions- https://thejns.org/spine/view/journals/j-neurosurg-spine/32/1/article-p1.xml
- Yadla S, Ratliff JK, Harrop JS. Whiplash: diagnosis, treatment, and associated injuries. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2008 Mar;1(1):65-8. doi: 10.1007/s12178-007-9008-x. PMID: 19468901; PMCID: PMC2684148.
- Huang CY, Tsai YH, Hong YH, Hsieh SL, Huang RH. Characterization and Antioxidant and Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme (ACE)-Inhibitory Activities of Gelatin Hydrolysates Prepared from Extrusion-Pretreated Milkfish (Chanos chanos) Scale. Mar Drugs. 2018 Sep 22;16(10):346. doi: 10.3390/md16100346. PMID: 30248998; PMCID: PMC6213483.
- Peng B, DePalma MJ. Cervical disc degeneration and neck pain. J Pain Res. 2018 Nov 14;11:2853-2857. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S180018. PMID: 30532580; PMCID: PMC6241687.
- Al Khalili Y, Ly N, Murphy PB. Cervicogenic Headache. [Updated 2022 Oct 3]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507862/





