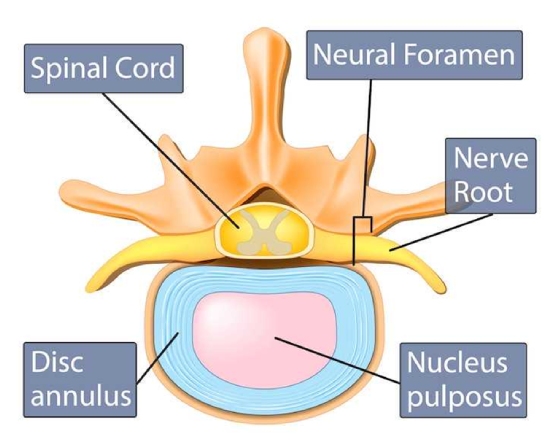
ANATOMY OF DISC
- Nucleus pulposus is the jelly like mass bounded by the annulus. It is rich in proteoglycans and is responsible in maintaining the water content of the disc
- Annulus Fibrosus is the lamellar layer bounding the nucleus pulposus and is rich in collagen fibres.
STAGES OF PROGRESSION – DISC PROLOAPSE/ HERNIATION
Bulging disc
Extension of disc tissue beyond the the margins of the ring apophyses, throughout the circumference is described as bulging.
- Diffuse bulging is produced by small tears in the annulus fibrosis.
- Asymmetric bulging is produced by a 25% or greater portion of the disc adapting to the adjacent deformity.
Disc bulge should not be confused with disc herniation as the annular covering is still intact in a disc bulge unlike a herniation.
Disc Herniation
Focal displacement of the disc material < 25% of the disc circumference , beyond the confines of the intervertebral disc space represents a disc herniation.
Contained herniated discs have an outer covering of annulus fibres and the posterior longitudinal ligament whereas Uncontained herniated discs lack the annulus covering. Contained herniations present with smooth margins on the protrusions.
Disc Protrusion and Extrusion
It is described as Protrusion when the distance between the edges of the disc herniation is lesser than the distance between the edges of the base.
Disc Extrusion is said to be present when the distance between the edges of the disc material is greater than the distance at the base.
Extrusion is almost always associated with a defect in the annulus fibrosus and is usually noncontained.
Disc Migration
Migration indicates displacement of disc material away from the site of extrusion, regardless of whether it has broken down into fragments.
Disc Sequestration
The term sequestration signifies that the displaced disc material has lost continuity with the parent disc.
Intravertebral Disc herniation
Intravertebral herniation or Schmorl node is herniation of disc material in the vertical direction through a gap in the vertebral end plate.
CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT is usually the first line of treatment that is undertaken in most of the cases
- Physical therapy, exercise and gentle stretching to help relieve pressure on the nerve root
- Ice and heat therapy for pain relief
- Manipulation (such as chiropractic manipulation)
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen, naproxen or COX-2 inhibitors for pain relief
- Narcotic pain medications for pain relief
- Oral steroids to decrease inflammation for pain relief
- Traction and spinal decompression machines have been tried but have been advised against as per recent literature.
IMAGE GUIDED INTERVENTIONS are reserved for cases not responding favourably to conservative treatment. Disc bulge, protrusion and relatively smaller herniations should be definitely given a trial of image guided interventions.
- TRANSFORAMINAL INJECTIONS
- INTERLAMINAR EPIDURAL INJECTIONS
- CAUDAL EPIDURAL INJECTION
- OZONE NUCLEOLYSIS
- PLATELET RICH PLASMA
- STEM CELLS
AT ALLEVIATE, we follow a multidisciplinary approach involving which includes Comprehensive Platelet Rich Plasma with Prolotherapy to the lower back following Image guided Anti Inflammatory injections for pain and symptom control.
This is coupled with a structured back strengthening program, lifestyle modifications and inputs from Clinical Nutrition and Clinical Psychology.
Surgeries such as Microdiscectomy and Endoscopic Discectomy are
- usually reserved for patients not responding to Non Operative means.
- Patients exhibiting motor weakness
- Migrated, Extruded and Sequestered discs causing symptoms often need surgical intervention.