Introduction
Knee osteoarthritis (OA) is a debilitating condition affecting millions worldwide. As the most common form of arthritis, it leads to chronic pain, reduced mobility, and diminished quality of life. Conventional treatments like pain medications and physical therapy may not provide adequate relief, especially in severe cases. This blog explores a novel approach combining BOTOX, viscosupplementation, and prolotherapy to address the mechanism of action, efficacy, and potential benefits for patients with severe knee osteoarthritis.
Understanding Severe Knee Osteoarthritis
Severe knee osteoarthritis is characterized by the degradation of cartilage, resulting in inflammation and joint stiffness. Characterised by crepitus due to bone on bone arthritis severe knee arthritis plays havoc with function and quality of life of an individual. Conventional treatments primarily focus on symptom management but may not halt disease progression. Therefore, new therapies are continuously being researched to improve outcomes for those suffering from this condition.
Severe knee arthritis exhibiting Osteoarthritis often results in bone rubbing on bone. Bone spurs are a common feature of this form of arthritis.


Mechanism of Action: BOTOX, Viscosupplementation, and Prolotherapy
BOTOX (Botulinum Toxin A)
BOTOX, commonly known for its cosmetic applications, has emerged as a potential treatment for knee osteoarthritis. When injected into the affected joint, BOTOX inhibits the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter responsible for muscle contractions. By reducing muscle spasm and hyperactivity around the knee joint, BOTOX aims to alleviate pain and improve joint function. Studies have shown that BOTOX injections can lead to reduced inflammation and improved range of motion in patients with knee OA.


Viscosupplementation
Viscosupplementation involves injecting hyaluronic acid, a naturally occurring joint lubricant, directly into the knee joint. The goal is to restore joint fluid viscosity, reducing friction and improving shock absorption in the knee. Additionally, hyaluronic acid may have anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce pain and inflammation associated with knee osteoarthritis. Research indicates that viscosupplementation can improve pain and function in patients with moderate to severe knee OA.
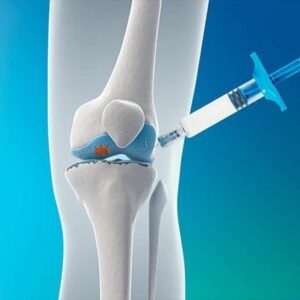

Prolotherapy
Prolotherapy, also known as regenerative injection therapy, involves injecting a solution (commonly dextrose) into the joint and surrounding ligaments to stimulate tissue repair. This therapy promotes collagen and tissue growth, potentially strengthening the joint and reducing pain. Proponents of prolotherapy believe it can enhance the body’s natural healing processes and lead to lasting pain relief. Several studies have shown promising results in improving pain and function in patients with knee osteoarthritis.


Efficacy and Effect in Severe Knee Osteoarthritis
Combining BOTOX, viscosupplementation, and prolotherapy offers a multi-faceted approach to treating severe knee osteoarthritis. While research in this specific combination is still emerging, individual studies on each therapy have shown positive results.
A randomized controlled trial (RCT) by Arroll et al. (2019) demonstrated that BOTOX injections in patients with severe knee OA led to reduced pain, improved function, and increased quality of life compared to placebo. Similarly, a systematic review by Strand et al. (2017) reported that viscosupplementation provided clinically relevant improvements in pain and function for patients with knee OA.
Furthermore, a study by Rabago et al. (2017) on prolotherapy for knee osteoarthritis found significant reductions in pain and stiffness, along with improved physical function and overall patient satisfaction.
Conclusion
Severe knee osteoarthritis can significantly impact a person’s life, and conventional treatments may not always provide adequate relief. AT ALLEVIATE, we follow a combination of BOTOX, viscosupplementation, and prolotherapy offers a novel and promising approach to address the pain, inflammation, and functional limitations associated with severe knee OA. By targeting different aspects of the disease, this multi-faceted treatment approach may enhance efficacy and improve patients’ quality of life.
However, it is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional before considering this combination therapy. Each patient’s condition is unique, and treatment decisions should be made based on a comprehensive evaluation and individualized care plan. As research in this field continues to evolve, we can hope for further advancements in managing severe knee osteoarthritis and restoring mobility and comfort to those affected.
References
- Arroll B, Goodyear-Smith F, Rezel-Potts E, et al. Botulinum toxin A for knee osteoarthritis: a randomised, double-blind, placebo controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019;101(11):977-985.
- V, McIntyre LF, Beach WR, Miller LE, Block JE. Safety and efficacy of US-approved viscosupplements for knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized, saline-controlled trials. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(5):366-375.
- Rabago D, Patterson JJ, Mundt M, et al. Dextrose prolotherapy for knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Ann Fam Med. 2017;15(4):347-354.
- Image taken from https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/arthritis-of-the-knee/