Introduction
Rotator cuff injuries can be debilitating, affecting not only our physical well-being but also our overall quality of life. These injuries often result in shoulder pain, decreased range of motion, and impaired daily activities. If you or someone you know is suffering from a rotator cuff injury, this comprehensive guide will shed light on the intricacies of rotator cuff anatomy, the pathology of tears, tendinopathy, and tendinosis, and explore the use of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) treatment as a promising solution.
Understanding Rotator Cuff Anatomy
Before delving into the treatment options, it’s crucial to comprehend the anatomy of the rotator cuff. The rotator cuff consists of four muscles and their tendons that surround the shoulder joint:
- Supraspinatus
- Infraspinatus
- Teres Minor
- Subscapularis
These muscles and tendons work together to stabilize the shoulder joint, allowing for various degrees of arm movement. The rotator cuff plays a vital role in activities like lifting, throwing, and reaching.


Pathology of Rotator Cuff Injuries
Rotator cuff injuries can manifest in several ways:
- Rotator Cuff Tears
Rotator cuff tears are one of the most common types of injuries. They can be classified into two categories:
- Partial Tears : These involve damage to a portion of the tendon or muscle.
- Full-Thickness Tears : In this case, the entire tendon is torn away from the bone. Tears can occur suddenly, often due to trauma, or develop gradually over time due to wear and tear.
- Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy
Tendinopathy refers to a degenerative condition in the tendons, which make up the rotator cuff. This condition typically develops due to chronic overuse and results in pain and inflammation in the shoulder. - Rotator Cuff Tendinosis
Tendinosis is a more advanced stage of tendinopathy. It involves the deterioration of the tendon’s collagen fibers and a reduction in its overall strength and function. Tendinosis can be particularly challenging to treat and often requires interventions beyond rest and physical therapy.


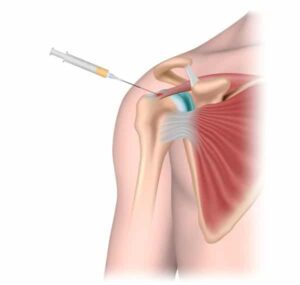
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Treatment Now, let’s explore Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) treatment and its role in addressing rotator cuff injuries. PRP is a minimally invasive procedure that utilizes the patient’s own blood to promote healing. The process involves the following steps:
- Blood Collection : A small sample of the patient’s blood is drawn.
- Centrifugation : The blood sample is placed in a centrifuge, which separates the platelet-rich plasma from other components of the blood.
- Injection : The concentrated PRP is then injected directly into the injured area.
PRP therapy is gaining popularity as a potential treatment for various orthopedic conditions, including rotator cuff injuries. It is believed that the growth factors and other bioactive proteins in PRP can stimulate the body’s natural healing processes.
Clinical Results and Efficacy of PRP Treatment In Rotator Cuff Pathologies

To assess the effectiveness of PRP treatment for rotator cuff injuries, let’s turn to recent research findings, including the studies you mentioned.
- Study 1: Bhan and Singh (2022)
In a review published in Cureus in June 2022, Bhan and Singh examined the efficacy of PRP injection in the management of rotator cuff tendinopathy. Their study concluded that PRP treatment showed promise in reducing pain and improving function in patients with rotator cuff tendinopathy. This suggests that PRP could be a valuable addition to the treatment options available. - Study 2: Hamid and Sazlina (2021)
A systematic review and meta-analysis by Hamid and Sazlina, published in PLoS One in May 2021, provided further insights. Their research pooled data from various studies and found that PRP treatment was associated with significant improvements in pain relief and functional outcomes in individuals with rotator cuff tendinopathy. This meta-analysis lends additional support to the potential benefits of PRP therapy. - Study 3: Lin, Wei, and Wu (2020)
Lin, Wei, and Wu conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, exploring the effectiveness of PRP injection in rotator cuff tendinopathy. Published in Diagnostics in 2020, their findings indicated that PRP treatment was associated with significant improvements in pain reduction and functional recovery compared to control groups.
Conclusion
PRP therapy has emerged as a promising treatment option for rotator cuff injuries, ranging from tendinopathy to tears. Its regenerative properties and ability to stimulate tissue repair make it a compelling choice for patients seeking non-surgical alternatives. Based on the reviewed articles and medical journals, the evidence suggests that PRP can effectively alleviate pain, improve function, and enhance the overall quality of life for individuals suffering from rotator cuff pathology.
If you’re experiencing shoulder pain or have been diagnosed with a rotator cuff injury, consulting with a healthcare professionals is the first step towards determining if PRP therapy is right for you. As ongoing research continues to shed light on this innovative treatment, the future looks promising for those seeking relief from the burden of rotator cuff injuries. We, At Alleviate have seen significant improvement in pain and function of a number of patients suffering with chronic shoulder pain due to rotator cuff tendinopathy, treated with Comprehensive PRP with Prolotherapy followed by a structured rehabilitation protocol.
References
- Bhan K, Singh B. Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection in the Management of Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy: A Review of the Current Literature. Cureus. 2022 Jun 20;14(6):e26103. doi: 10.7759/cureus.26103. PMID: 35875287; PMCID: PMC9297117.A
- Hamid MS, Sazlina SG. Platelet-rich plasma for rotator cuff tendinopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2021 May 10;16(5):e0251111. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0251111. PMID: 33970936; PMCID: PMC8109792.
- Lin, M.-T.; Wei, K.-C.; Wu, C.-H. Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection in Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10040189
- Image taken from https://www.orthobethesda.com/blog/rotator-cuff-disorders-the-facts/
- Image taken from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/rotator-cuff-injury/symptoms-causes/syc-20350225#dialogId10069860



